Fig. 8. Proposed model for the neuroprotection by MLA, 4R, and BMI.
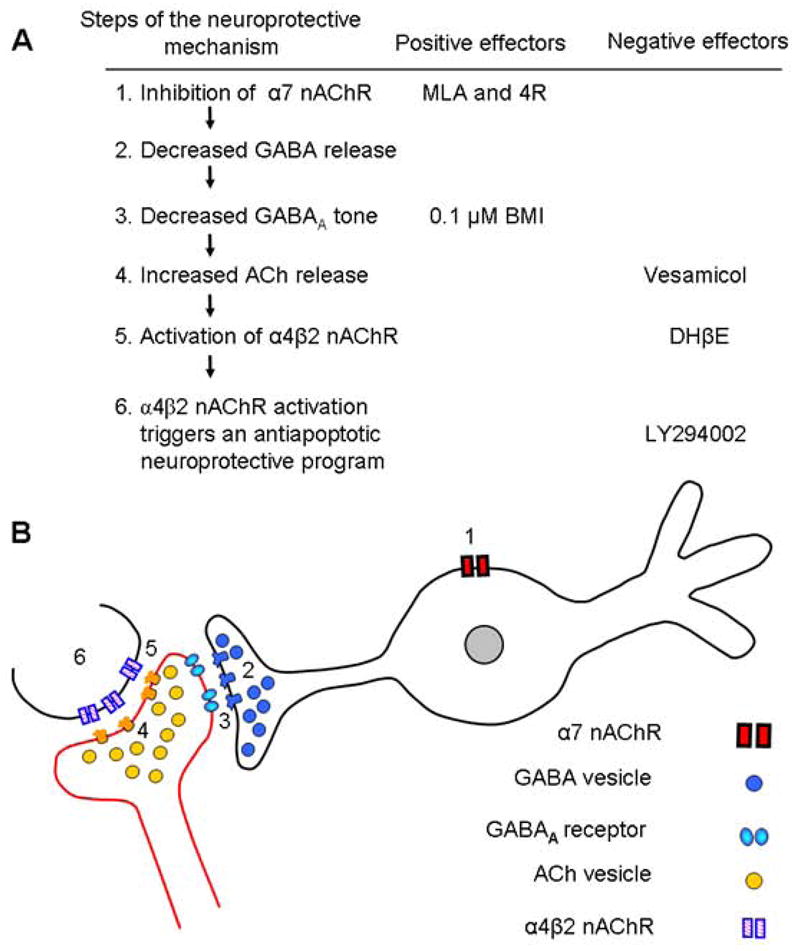
A) Proposed sequence of steps and the inhibitors used to explore them. 1) MLA and 4R inhibit α7 nAChR on GABAergic interneurons or septal afferents. 2) Decreased α7 activity reduces GABA release. 3) The hyperpolarizing tone decreases either because of reduced GABA release or because of the presence of the antagonist BMI. 4) Reduced inhibition on cholinergic terminals allows for more ACh release. Vesamicol blocks this pathway by blocking the synaptic release of ACh. 5) The enhanced ACh release activates the α4β2 nACh receptors. DHβE, a selective antagonist of α4β2 blocks this step. 6) Activation of α4β2 receptors triggers the phosphoinositide 3-kinase neuroprotective cascade, which is blocked by LY294002. Positive or negative effector refers to compounds that cause or reverse the neuroprotection.
B) Proposed localization of receptors and synaptic elements. Inhibition of α7 receptors (1) on GABAergic interneurons or GABAergic terminals attenuates GABA release (2) and decreases the GABAergic tone (3) on incoming cholinergic afferents. The decreased GABAergic tone is mimicked by BMI, a GABAA antagonist. Weaker GABAergic tone (3) disinhibits the synaptic release of ACh (4) and increases the activation of α4β2 (5) on terminals innervating pyramidal neurons or directly on pyramidal neurons. The icons representing receptors and synaptic vesicles are presented in the top to bottom sequence in which they are presumed to act in this mechanism.
