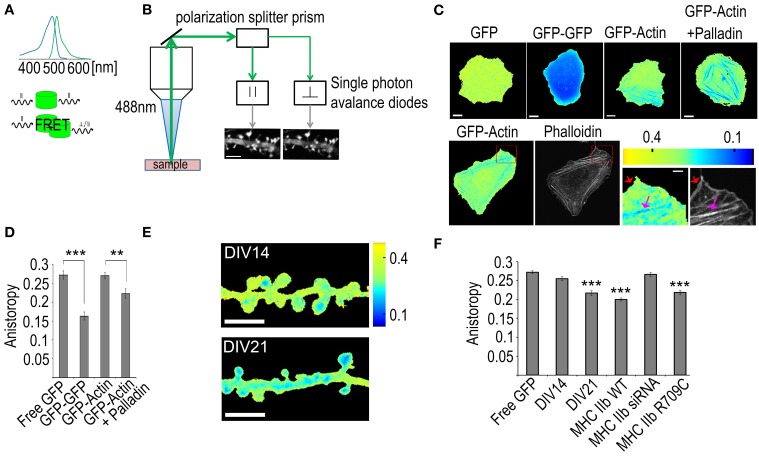
Figure 6.
Using fluorescence anisotropy measurements to study actin bundling. (A) Upper panel: the absorption and emission spectra of GFP. Lower panel: a schematic of the differences between direct emission and FRET-mediated emission where the polarization information is lost. (B) The signal path of the emission. The emission signal is first directed to a polarization splitter prism that separates the signal having polarization parallel to the excitation laser from the perpendicular one. The signal is then directed to two single photon avalanche diode detectors that form accurate intensity images of the sample. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) Upper panel: Fluorescence anisotropy images of U2OS cells transfected with GFP, GFP-GFP, GFP-actin or GFP-actin + palladin-mCherry, Scale bars 10 μm. Lower panel: first frame: a fluorescence anisotropy image of a U2OS cell transfected with GFP-actin, second frame: the same cell with F-actin stained with phalloidin-Alexa 594. The two last frames: enlargements of the area indicated by the red rectangle in the fluorescence anisotropy and the phalloidin images, red arrows indicate the non-bundled F-actin in the cell cortex and the pink arrows indicate the bundled stress fibers. Scale bars: whole cell images 10 μm, enlarged sections 2 μm. All the fluorescence anisotropy images are pseudocolored according to the scale in the upper right corner of the lower panel. (D) Mean GFP anisotropy values of whole U2OS cells transfected with free GFP (n = 18 cells), GFP-GFP (n = 15 cells), GFP-actin (n = 23 cells) or GFP-actin with palladin-mCherry (n = 13 cells). ANOVA shows that there are statistically significant differences between groups in fluorescence anisotropy F(3, 65) = 24.335, p < 0.0001. Free GFP (M = 0.27) had statistically significant (p < 0.0001) higher values than GFP-GFP (M = 0.16), likewise GFP-actin (M = 0.27) had higher values than GFP-GFP. Free GFP had statistically significant (p < 0.01) higher values than GFP-actin + palladin (M = 0.22), likewise GFP-actin + Palladin had higher values than GFP-GFP and, GFP-actin had higher values than GFP-actin + Palladin. All graphs mean ± s.e.m. (E) Anisotropy images of DIV14 and DIV21 rat hippocampal neurons color-coded according to the scale on the right. Scale bar, 5 μm. (F) Comparison of the mean anisotropy values from dendritic spines of DIV14 hippocampal neurons or DIV21 hippocampal neurons (DIV21). DIV21 neurons were transfected with GFP-actin n = 66 spines. DIV14 neurons were transfected with various constructs: (1) free GFP (marked as free GFP) n = 49 spines, (2) GFP-actin (marked as DIV14) n = 77 spines, (3) GFP-actin and mCherry-MHC IIb n = 61 spines, (4) GFP-actin and MHC IIb siRNA n = 69 spines, (5) GFP-actin and mCherry-MHC IIb R709C n = 41 spines, (6) ANOVA showed that there are statistically significant differences in anisotropy between groups F(8, 574) = 20.641, p <0.0001. DIV14 (M = 0.25) had higher values (p < 0.0001) than DIV21 (M = 0.21), MHC-WT (M = 0.20), MHC IIb R709C (M = 0.21). All graphs mean ± s.e.m; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.