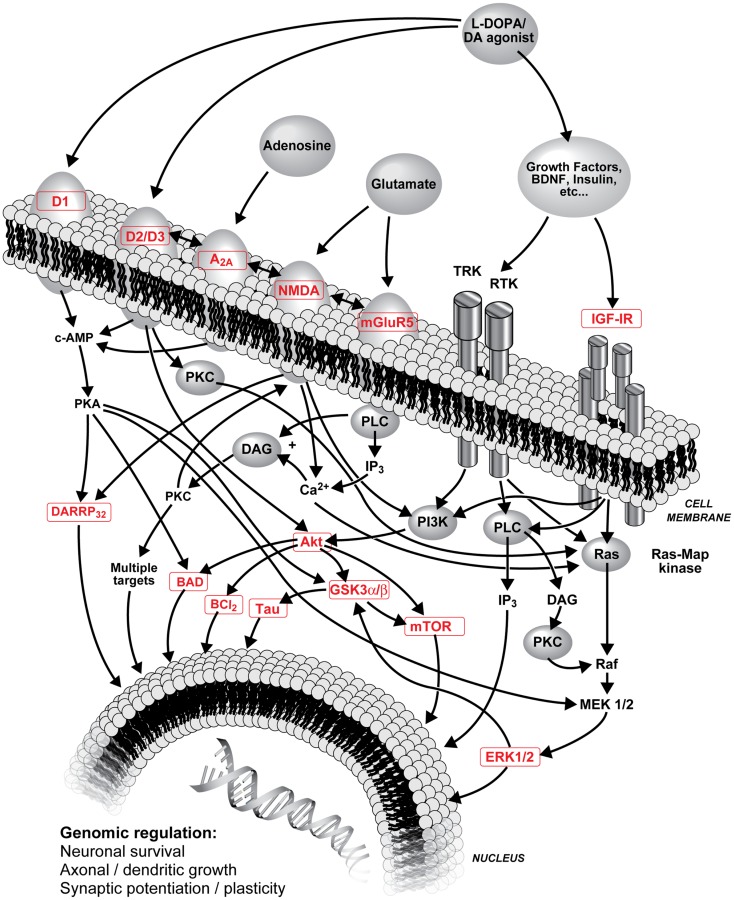
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of l-DOPA (metabolized into DA) and DA agonist treatments on striatal DA neurotransmission, interactions of striatal DA, adenosine, glutamate, and opioids in GABAergic neurons and possible sequence of events leading to LID. Numerous interactions are known and are not all included; the focus of this figure is on PI3K and MAPK pathways. A2A, adenosine A2A receptor; Akt, protein kinase B; BAD, Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Ca2+, calcium ion; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; D1/D2/D3, D1/D2/D3 DA receptor; DA, dopamine; DARPP-32, DA and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein with molecular weight 32; DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; IGF-IR, type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; l-DOPA, levodopa (l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine); MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mGlu5, metabotropic glutamate type 5 receptor; mTor, mammalian target of rapamycin; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; Ras, proto-oncogene protein p21; Raf, proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinases; Tau, microtubule-associated protein tau; TRK, tropomyosin receptor kinase.