Figure 1. Chemotactic factors involved in eosinophil infiltration in the GI track.
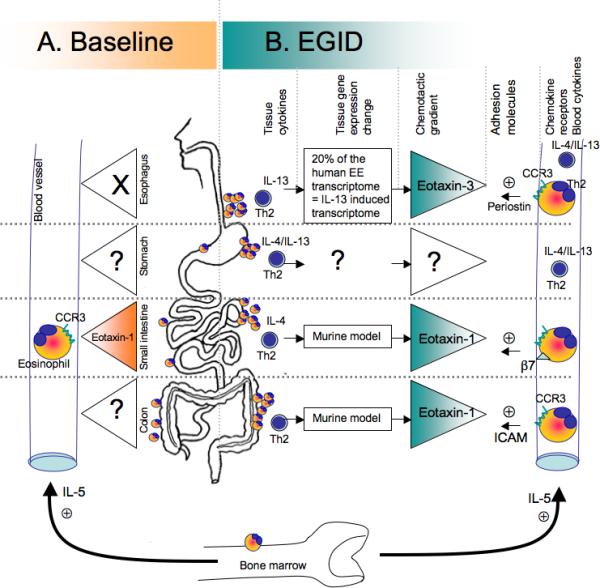
A. Hematopoietic cells are present at baseline in all segments of the GI track. The distribution of eosinophils differs from one segment to another. Basal IL-5 level allows maturation and survival of eosinophils. In the esophagus, no eosinophils are seen, however, the eosinophil levels in the tissue increase from the stomach to the colon. Eotaxin-1 expression in the GI tract and CCR3 expression on the eosinophils are involved in the eosinophilia in the jejunum. B. Eosinophil infiltration in EGID has been associated to Th2 diseases and increased Th2 cytokine production (IL-4, IL-13), has been shown in the blood in EE, EGE, and EG patients. CCR3 expressed on eosinophils have been shown critical for intestinal and esophageal eosinophilic diseases. The eotaxins 1 and 3 are responsible in part for EGID in the intestines and the esophagus, respectively. Others molecules, such the adhesion molecules B7 integrin and ICAM have been shown involved in EGE and EC models but no data document their role EE and EG.
