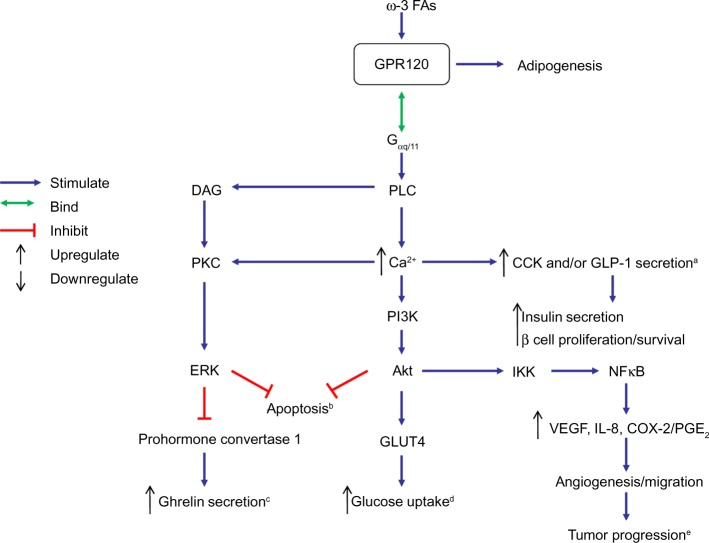
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the potential mechanism by which GPR120-Gαq/11 signaling may affect various physiological and pathological processes.
Notes: Binding of ω-3 FA-activated GPR120 to Gαq/11 stimulates PLC, leading to an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), which may influence diverse physiological processes, such as CCK, GLP-1, and ghrelin secretion, glucose uptake, tumor progression, and apoptosis. aCCK and/or GLP-1 secretion in taste bud cells, intestinal tract and STC-1 cells. bApoptosis of STC-1 cells. cGhrelin secretion of stomach. dGlucose uptake of adipocytes. eTumor progression of colorectal carcinoma.
Abbreviations: ω-3 FAs, ω-3 fatty acids; Akt, protein kinase B; CCK, cholecystokinin; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; FA, fatty acid; Gαq/11, heterotrimeric G-protein; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GLUT4, glucose transporter 4; GPR120, G-protein coupled receptor 120; IKK, IκB kinase; IL-8, interleukin 8; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; PLC, phospholipase-C; PKC, protein kinase C; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; STC-1, mouse intestinal enteroendocrine cell line; Ca2+, intracellular calcium level.