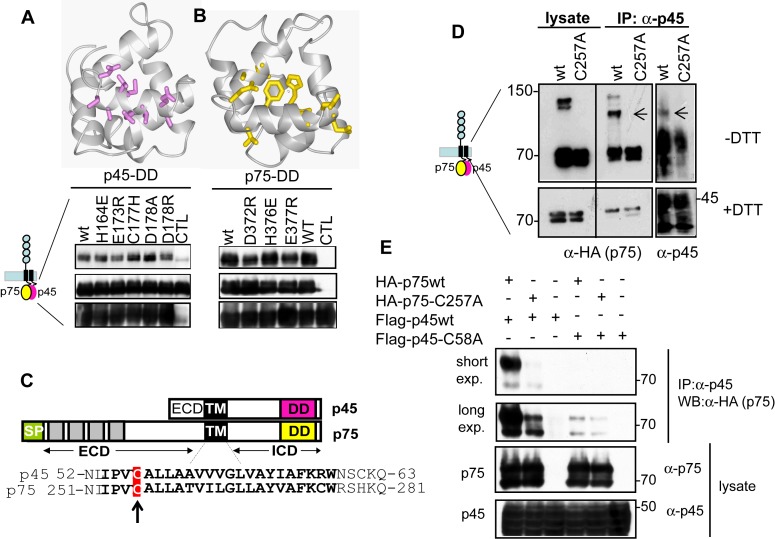
Figure 7. p75/p45 interaction is promoted by DD and TM domain.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments of wild-type or mutant p45 with Myc-p75 in HEK293 cells. p45 mutants show differential binding to p75. The p75DD-dependent chemical shift changes of p45DD are mapped onto the 3D structure of p45DD. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments of wild-type or p75 mutants with Flag-p45 in HEK293 cells showed differential binding to p45. The p45DD-dependent chemical shift changes of p75DD are mapped onto the 3D structure of p45DD. (C) Protein sequences of p75 and p45 TM domains are highly conserved. The conserved cysteine residue is highlighted in a red box. (D) The cysteine residues in the TM domain of both p75 and p45 form a covalent disulfide dimer between p75 and p45. Co-immunoprecipitations of either p75 wild-type or the p75 TM domain mutant (p75-C257A) with p45 wild type were analyzed in HEK293 cells and in reducing and nonreducing SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot. p75 and p45 form a heterodimer sensitive to DTT (arrow). (E) Co-immunoprecipitations of either p75 wild type or the p75 TM domain mutant (p75-C257A) with p45 wild type or p45 C58A mutant were analyzed in HEK293 cells, indicating that both p75-C257A and p45-C58A TM domain mutants diminish the interaction between p75 and p45.