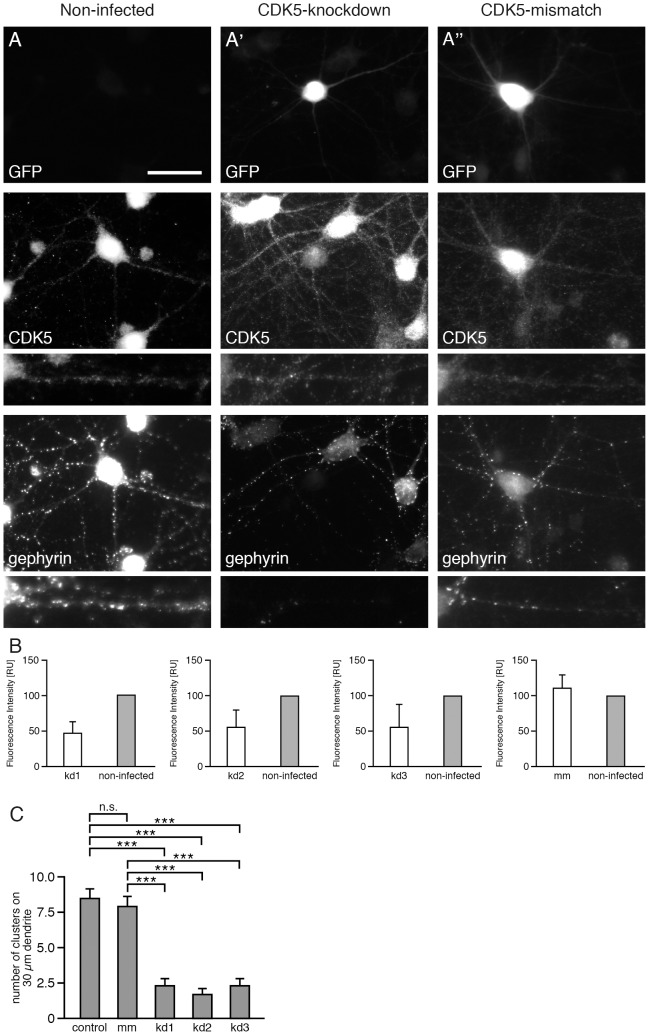
Figure 1. CDK5 knockdown virus infection results in reduced CDK5 expression and reduced numbers of phospho-gephyrin clusters in cultured hippocampal neurons.
Hippocampal neurons (div14) were stained with anti-GFP antibodies to detect infected neurons (upper panel), with anti-CDK5 antibody to quantify CDK5 expression levels (middle panel) and with the phosphospecific anti-gephyrin mAb7a antibody (lower panel). (A) Non-infected cells; (A') CDK5-knockdown; (A'') control shRNA (CDK5-mismatch). Neurons were infected with the indicated viruses at div6. The scale bar represents 15 µm. (B) Quantification of CDK5 fluorescence intensities of neurons infected with three different CDK5 knockdown viruses (kd1, kd2 and kd3). CDK5 knockdown cells were compared to non-infected neurons. n = 3, mean ± SD (C) Quantification of mAb7a cluster numbers of hippocampal neurons infected with three different CDK5 knockdown viruses (kd1, kd2, kd3) compared to non-infected and control shRNA (mismatch). 30 cells from n = 4 independent cultures (for each of non-infected, mismatch, kd2, kd1) or 30 cells from n = 3 independent cultures (kd3), mean ± SE, ANOVA with post-hoc test, ***P<0.001.