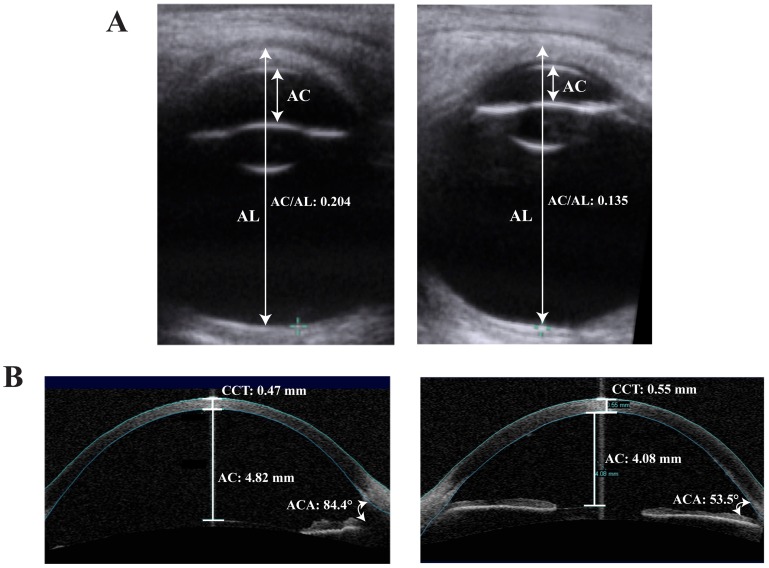
Figure 3. Comparison between biometry of X-linked megalocornea and congenital glaucoma.
(A) AC, anterior chamber depth (back of cornea to front of lens); AL, axial length (anterior corneal surface to vitreo-retinal interface at the back of the macular). Transverse B-Mode ultrasound scans demonstrate higher ratio of the AC to AL in megalocornea, 0.204 (left) than congenital glaucoma, 0.135 (right). (B) Ocular coherence tomography (OCT) images comparing megalocornea (left) and arrested congenital glaucoma (right). Although there is enlargement of the anterior segment in both conditions, patients with megalocornea tend to have a greater anterior chamber (AC) depth, lower central corneal thickness (CCT), and deeper anterior chamber angles (ACA) than congenital glaucoma patients.