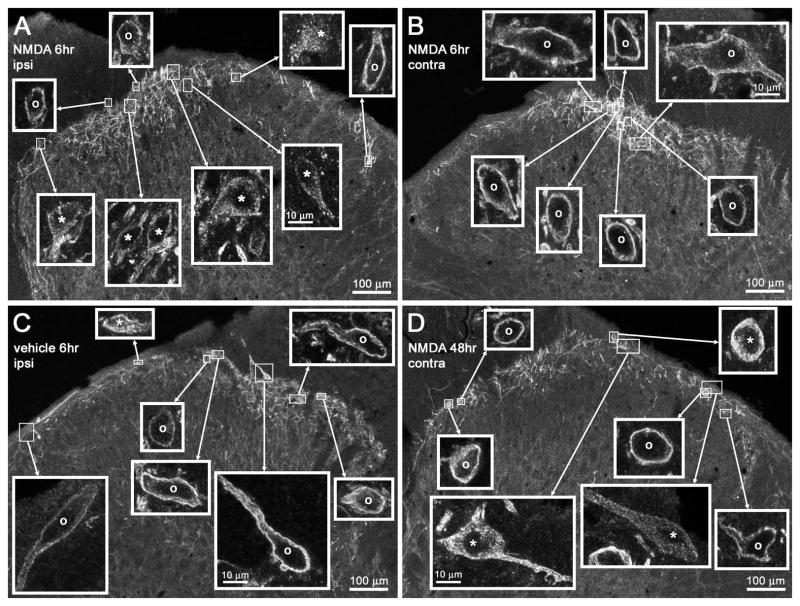
Figure 9.
Confocal images of NK1R neurons in lamina I after CCI. Rats underwent unilateral CCI of the sciatic nerve and received intrathecal (A, B and D) NMDA (10 nmol with 10 nmol D-Ser) or (C) vehicle at the times indicated. Images were taken from the L4 spinal segment. (A and B) Intrathecal NMDA 6 h after CCI resulted in (A) abundant NK1R internalization ipsilateral to CCI but (B) no NK1R internalization contralaterally. (C) Intrathecal vehicle 6 h after CCI did not result in any NK1R internalization ipsilateral to CCI. (D) Intrathecal NMDA 48 h after CCI resulted in some NK1R internalization contralateral to CCI. Main panels: images taken with a 10× objective; voxel size of 830 × 830 × 5983 nm and three confocal planes. Insets: images panels taken with a 63× objective of the lamina I neurons indicated by the frames in the main panel; voxel size of 132 × 132 × 383 nm and four to six confocal planes. Adjustments in the gamma of the images in the insets were made to ensure that the staining of neurons was of similar intensity; the uncorrected intensity can be seen in the main panel images. Neurons with NK1R internalization are indicated with ‘*’ and neurons without internalization by ‘o’. Scale bars, 100 μm (main panels), 10 μm (insets).