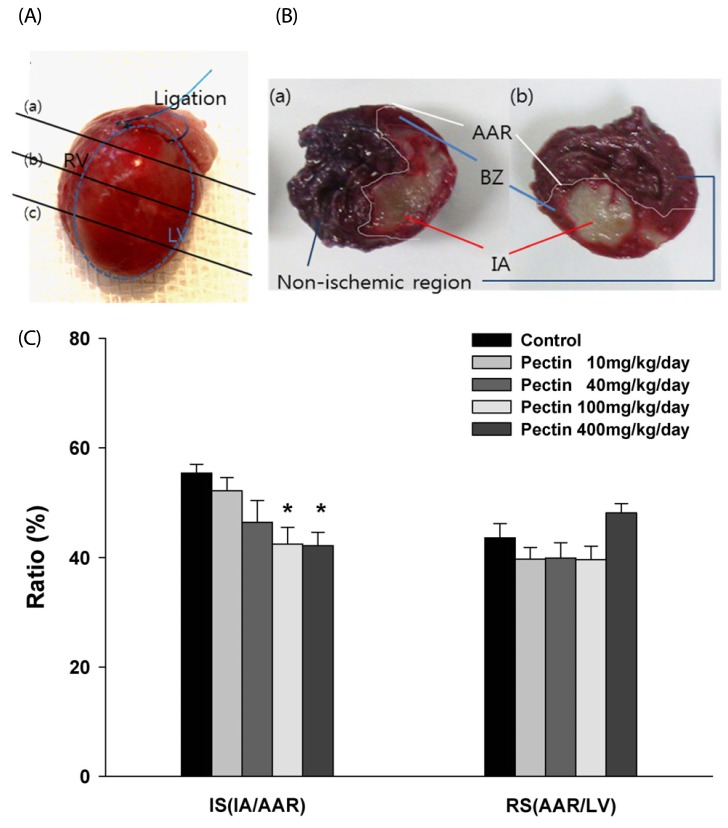
Fig. 1.
Effect of apple pectin (AP) on infarct size in rats. Rats underwent 30 min-ischemia/3 hr-reperfusion, followed by injection of Evans blue through the jugular vein, from which area at risk (AAR) and non-ischemic region were defined as the area with Evans blue not infiltrated and the area with Evans blue infiltrated, respectively. (A) The myocardium was then excised into four pieces, approximately 3 mm thick, and two pieces (a-b and b-c) were used for quantification of infarct area. (B) The slices were stained with TTC, from which area at risk (AAR), infarct area (IA), border zone (BZ), and non-ischemic (Non-ischemic) heart tissue were defined: (a) Vehicle-treated control group; (b) Extract-treated group. C. Infarct size [IS(IA/AAR)] and risk size [(RS(AAR/LV)) were expressed as a percentage of IA to AAR and of AAR to the left ventricle (LV), respectively. AP (with 10, 40, 100, and 400 mg/kg/day) was fed for three days prior to occlusion. The numbers of rats used in the control and AP (with 10, 40, 100, and 400 mg/kg/day)-treated groups were 5, 8, 6, 5, and 7, respectively. *P < 0.05 vs. control group.