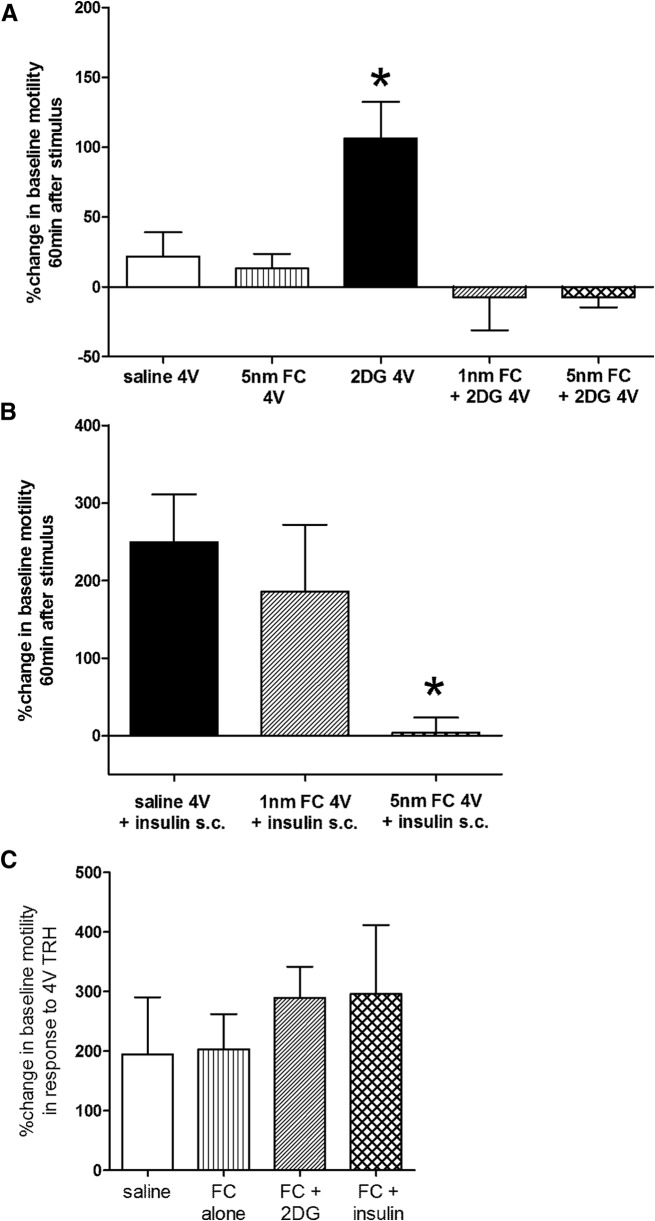
Figure 6.
Statistical comparisons of motility indices. A, 2DG applied to the 4V significantly increases gastric motility compared with control (saline 4V). Although 4V FC alone has no effect on gastric motility, either dose of 4V FC (1 or 5 nmole) blocks the pro-motility effects of 4V 2DG (N = 20; Dunnett's post hoc comparisons; *p ≤ 0.05). B, Subcutaneous insulin (10 units/kg) produces a dramatic increase in motility index. Although 1 nmole 4V FC effects to reduce this insulin effect are not significant, 5 nmole FC was able to block the increase in gastric motility at the 60 min time point (N = 15; Dunnett's post hoc comparisons; *p ≤ 0.05). C, 4V application of TRH 3 h after other 4V challenges caused a large increase in MI that was not different across the saline, FC, or FC + 2DG groups. This final challenge was administered to verify that the vago-vagal neurocircuitry involved in gastric function was not compromised by surgical preparations or exposure to FC. Note that TRH was not applied to the 2DG alone cases because gastric motility was still elevated at this time and there was no concern about integrity of vago-vagal circuit.