Abstract
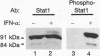
One of the most important cytokines involved in immune response regulation is interleukin 2 (IL-2), a potent activator of the proliferation and function of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The mechanisms by which the effects of IL-2 are propagated within cells are not understood. While the binding of IL-2 to its receptor was recently shown to lead to the activation of two kinases, Jak-1 and Jak-3, subsequent steps in the signaling pathway to the nucleus that lead to the activation of specific genes had not been characterized. Since many cytokines that activate Jak kinases also lead to the tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of members of the Stat family of transcription factors, the ability of IL-2 to trigger Stat phosphorylation was examined. Exposure of activated human T lymphocytes or of a natural killer cell line (NKL) to IL-2 leads to the phosphorylation of Stat1 alpha, Stat1 beta, and Stat3, as well as of two Stat-related proteins, p94 and p95. p94 and p95 share homology with Stat1 at the phosphorylation site and in the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, but otherwise are immunologically distinct from Stat1. These Stat proteins were found to translocate to the nucleus and to bind to a specific DNA sequence. These findings suggest a mechanism by which IL-2 binding to its receptor may activate specific genes involved in immune cell function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonni A., Frank D. A., Schindler C., Greenberg M. E. Characterization of a pathway for ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling to the nucleus. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1575–1579. doi: 10.1126/science.7504325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussiotis V. A., Barber D. L., Nakarai T., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Bernstein G. M., D'Andrea A. D., Ritz J., Nadler L. M. Prevention of T cell anergy by signaling through the gamma c chain of the IL-2 receptor. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1039–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.7973657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D. The hematopoietin receptor superfamily. Cytokine. 1993 Mar;5(2):95–106. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(93)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. W., Farrar W. L. Interleukin 2 and diacylglycerol stimulate phosphorylation of 40 S ribosomal S6 protein. Correlation with increased protein synthesis and S6 kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4624–4630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Wakao H., Mundt M., Groner B. Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of Stat5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4361–4369. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Gress R. E., Lucas P. J., Horak E. M., Waldmann T. A., Bolen J. B. T-lymphocyte interleukin 2-dependent tyrosine protein kinase signal transduction involves the activation of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Ho T. C., Brasseur M., McKnight S. L. An interleukin-4-induced transcription factor: IL-4 Stat. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1701–1706. doi: 10.1126/science.8085155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. A., Kawamura M., Kirken R. A., Chen Y. Q., Blake T. B., Shibuya K., Ortaldo J. R., McVicar D. W., O'Shea J. J. Phosphorylation and activation of the Jak-3 Janus kinase in response to interleukin-2. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):151–153. doi: 10.1038/370151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura M., McVicar D. W., Johnston J. A., Blake T. B., Chen Y. Q., Lal B. K., Lloyd A. R., Kelvin D. J., Staples J. E., Ortaldo J. R. Molecular cloning of L-JAK, a Janus family protein-tyrosine kinase expressed in natural killer cells and activated leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6374–6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Chung J., Fiorentino D. F., Flanagan W. M., Blenis J., Crabtree G. R. Rapamycin selectively inhibits interleukin-2 activation of p70 S6 kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):70–73. doi: 10.1038/358070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Kawahara A., Fujii H., Nakagawa Y., Minami Y., Liu Z. J., Oishi I., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Ihle J. N. Functional activation of Jak1 and Jak3 by selective association with IL-2 receptor subunits. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1045–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.7973659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.181845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Russell S. M., Mess S. A., Friedmann M., Erdos M., Francois C., Jacques Y., Adelstein S., Leonard W. J. Heterodimerization of the IL-2 receptor beta- and gamma-chain cytoplasmic domains is required for signalling. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):330–333. doi: 10.1038/369330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. H., Lord J. D., Greenberg P. D. Cytoplasmic domains of the interleukin-2 receptor beta and gamma chains mediate the signal for T-cell proliferation. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):333–336. doi: 10.1038/369333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Sabath D. E., Hoover R. G., Prystowsky M. B. Recombinant interleukin 2 regulates levels of c-myc mRNA in a cloned murine T lymphocyte. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3361–3368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Johnston J. A., Noguchi M., Kawamura M., Bacon C. M., Friedmann M., Berg M., McVicar D. W., Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O. Interaction of IL-2R beta and gamma c chains with Jak1 and Jak3: implications for XSCID and XCID. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.7973658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Miyajima A., Kaziro Y. Involvement of ras p21 protein in signal-transduction pathways from interleukin 2, interleukin 3, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, but not from interleukin 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3314–3318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya H., Yoneyama M., Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Matsumoto K., Taniguchi T. IL-2 and EGF receptors stimulate the hematopoietic cell cycle via different signaling pathways: demonstration of a novel role for c-myc. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90533-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Horvath C. M., Huang L. H., Qureshi S. A., Cowburn D., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon activation of the transcription factor Stat91 involves dimerization through SH2-phosphotyrosyl peptide interactions. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Darnell J. E., Jr A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1744–1746. doi: 10.1126/science.7690989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. B., Smith K. A. Interleukin-2 induction of T-cell G1 progression and c-myb expression. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.3523754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita T., Asao H., Ohtani K., Ishii N., Kumaki S., Tanaka N., Munakata H., Nakamura M., Sugamura K. Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL-2 receptor. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.1631559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torigoe T., Saragovi H. U., Reed J. C. Interleukin 2 regulates the activity of the lyn protein-tyrosine kinase in a B-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2674–2678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouche D., Robin P., Robillard O., Sassone-Corsi P., Harel-Bellan A. c-fos transcriptional activation by IL-2 in mouse CTL-L2 cells is mediated through two distinct signal transduction pathways converging on the same enhancer element. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2398–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt K. E., Mills G. B., Turck C. W., Imboden J. B. SH2-dependent association of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase 85-kDa regulatory subunit with the interleukin-2 receptor beta chain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5937–5943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B., Rapp U., App H., Greene M., Dobashi K., Reed J. Interleukin 2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of p72-74 Raf-1 kinase in a T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Miura O., Lai K. S., Cwik C., Liu E. T., Ihle J. N. Involvement of the Jak-3 Janus kinase in signalling by interleukins 2 and 4 in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):153–157. doi: 10.1038/370153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Quelle F. W., Thierfelder W. E., Kreider B. L., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N. Stat4, a novel gamma interferon activation site-binding protein expressed in early myeloid differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4342–4349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3 and Stat4: members of the family of signal transducers and activators of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4806–4810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmuidzinas A., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M., Smith K. A. Interleukin-2-triggered Raf-1 expression, phosphorylation, and associated kinase activity increase through G1 and S in CD3-stimulated primary human T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2794–2803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]