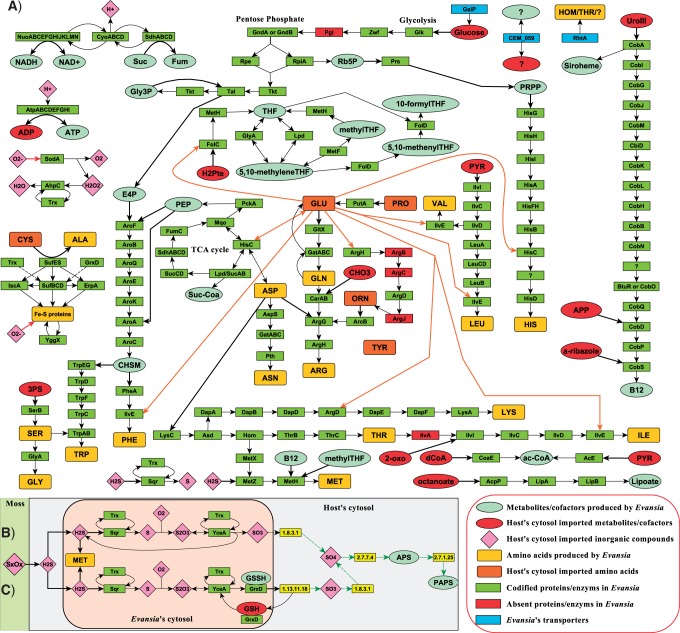
Fig. 6.—
Biosynthetic capabilities of Evansia. (A) Simplified graph showing the metabolic reconstruction for Evansia. (B) Putative H2S recycling pathway. (C) Putative H2S detoxification pathway. Amino acids are identified by the standard three letter code. Black arrows point the direction of the reaction. Black thick arrows represent inputs for a reaction. Orange thick arrows indicate reactions that need glutamate as input. Red arrows represent ROS interactions. Green arrows denote reactions produced by the host. Dashed arrows indicate poorly characterized or putative reactions. “?” denotes an unidentified protein/metabolite/compound. APP, (R)-1-amino-2-propanol O-2-phosphate; UroII, uroporphyrinogen-III; CHO3, bicarbonate; PYR, pyruvate; CHSM, chorismate; E4P, D-erythrose 4-phosphate; Rb5P, D-ribose 5-phosphate; PRPP, 5-phospho-α-D-ribose 1-diphosphate; Gly3P, D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate- H2Pte, 7,8-dihydropteroate; THF, tetrahydrofolate; CoA, coenzyme A; dCoA, 3'-dephospho-CoA; Ac-CoA, acetyl-CoA; Suc-Coa, succinyl-CoA; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; 3PS, 3-phospho-L-serine; O2−, reactive oxygen species; 2-oxo, 2-oxoglutarate; GSH, glutathione; GSSH, glutathione sulfide; APS, adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate; PAPS, phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate; SxOx, Sulfur oxidized forms.