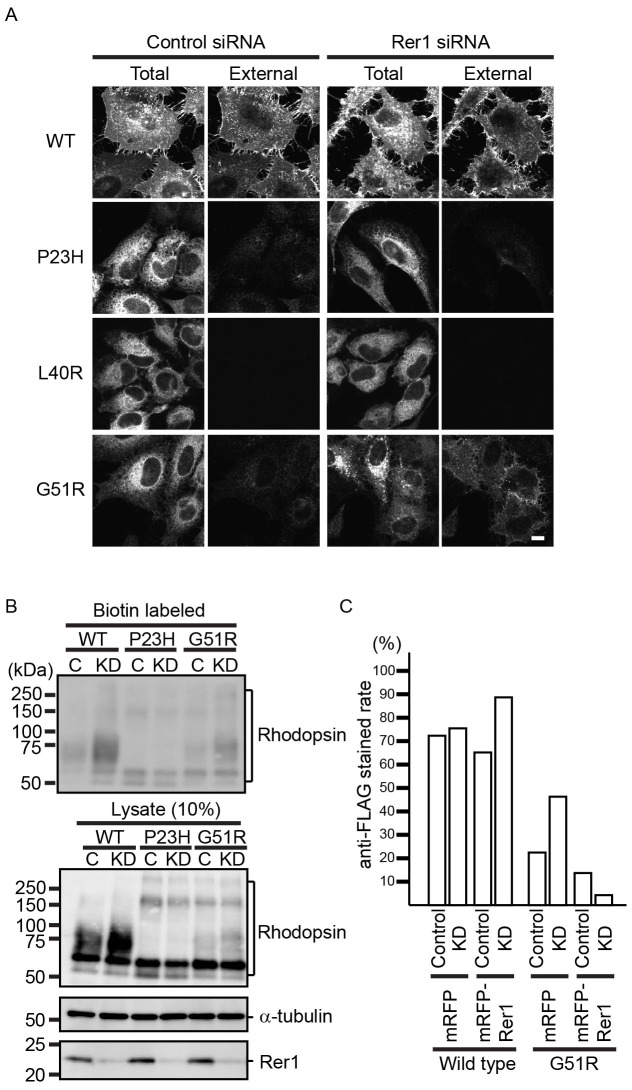
Figure 2. Rer1p contributes to the ER retention of G51R mutant rhodopsin.
(A) Loss of Rer1p increases the cell surface expression of G51R mutant rhodopsin. HeLa cells expressing each FLAG-rhodopsin-GFP construct were treated with control siRNA or Rer1 #1 siRNA for 72 h. Cells were fixed without permeabilization and stained with anti-FLAG antibody. The GFP signal and anti-FLAG staining indicate the localization of total and external rhodopsin, respectively. Bar: 10 μm. (B) Cell surface protein biotinylation assay. HeLa cells expressing each FLAG-rhodopsin-GFP construct were treated with control siRNA or Rer1 #1 siRNA for 72 h and biotinylated. Biotinylated proteins were then pulled down using streptavidin agarose and immunoblotted with an anti-GFP antibody. A fraction (10%) of the total cell lysate was also immunoblotted with anti-GFP (rhodopsin), anti-α-tubulin, and anti-Rer1p antibodies. Note that cropped western blots are shown and that full-length images are presented in the supplementary information. (C) The phenotype induced by Rer1 siRNA is specific to the knockdown of Rer1 expression. Cells were treated with control siRNA or Rer1 #1 siRNA for 72 h. After 48 h of siRNA transfection, cells were co-transfected with FLAG-rhodopsin-GFP and either mRFP or siRNA-resistant mRFP-canine Rer1. Cells were fixed without permeabilization and stained with anti-FLAG antibody. The graph indicates the ratio of anti-FLAG stained cells to the total number of cells.