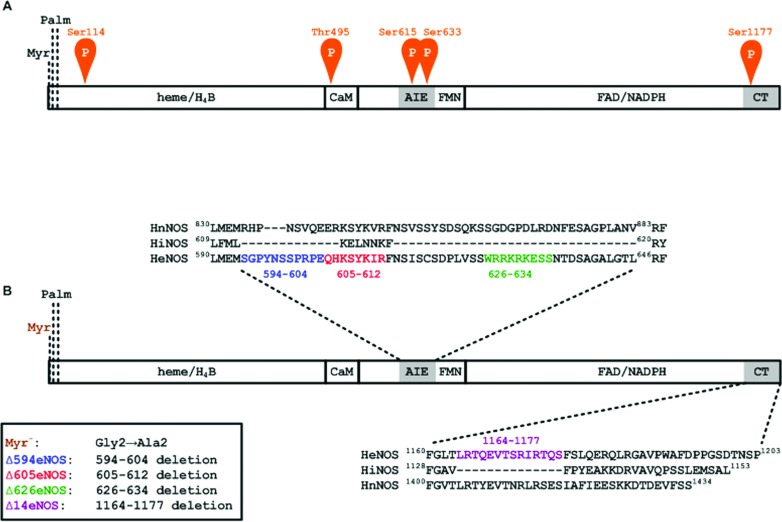
Figure 1. heNOS and the deletion constructs.
(A) The relative positions of phosphorylation sites in heNOS. Blocks indicate the binding sites for haeme, H4B, CaM, FMN, FAD and NADPH in eNOS. AIE and CT refer to the AIE and the C-terminal tail, respectively. The myristoylation site (Myr.) and palmitoylation sites (Palm.) are noted. Potential phosphorylation sites Ser114, Thr495, Ser615, Ser633 and Ser1177 are indicated. (B) Constructs for the eNOS deletion mutants. The sequences of the AIE and the C-terminal tail are shown above and below, respectively. The Δ594 is a deletion of the AIE region encompassing residues Ser594–Glu604 (shown in blue); Δ605 is a deletion of the AIE region encompassing residues Gln605–Arg612 (shown in red); Δ626 is a deletion of the AIE region encompassing residues Trp626–Ser634 (shown in green); Δ14 is a deletion of 14 amino acid residues at the C-terminal tail encompassing residues Leu1164–Ser1177 (shown in violet).