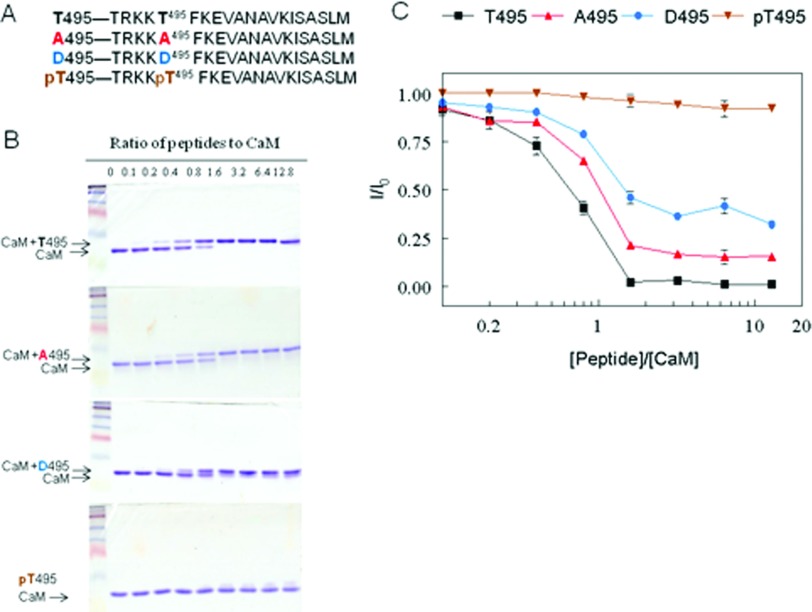
Figure 5. Interaction of synthetic CBD peptides with calcium/CaM.
(A) Peptide CBD sequences (residues 491–510, based on heNOS) with unmodified T495 (T495), phosphonull A substitution (A495, red colour), phosphomimetic substitution (D495, blue colour) and phosphorylated T495 (pT495, brown colour) are indicated. (B) The synthetic CBD variants were incubated with CaM (200 pmol) by increasing peptide:CaM molar ratios in the presence of 100 μM CaCl2 before electrophoresis. The samples were analysed on 18% non-denaturing gels and visualized with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. Representative Coomassie Brilliant Blue-stained gels of samples containing CaM and increasing molar ratios of T495, A495, D495 and pT495 are shown. The first lane in each gel contains CaM only, i.e., CBD/CaM ratio is 0. The rest CBD/CaM ratios were 0.1:1 (2nd lane), 0.2:1 (3rd lane), 0.4:1 (4th lane), 0.8:1 (5th lane), 1.6:1 (6th lane), 3.2:1 (7th lane), 6.4:1 (8th lane) and 12.8:1 (9th lane). CBD–CaM complexes and free CaM are denoted. (C) The relative amount of CaM on the gel at each peptide concentration (I) was determined by densitometry and normalized to CaM in the absence of peptide (I0). The data are plotted as the mean I/I0±S.D. (n=4) versus peptide:CaM ratio. The graph shows CaM with increasing peptide concentration described by the following symbols: ■, T495; ▲, A495; ●, D495 and ▼, pT495.