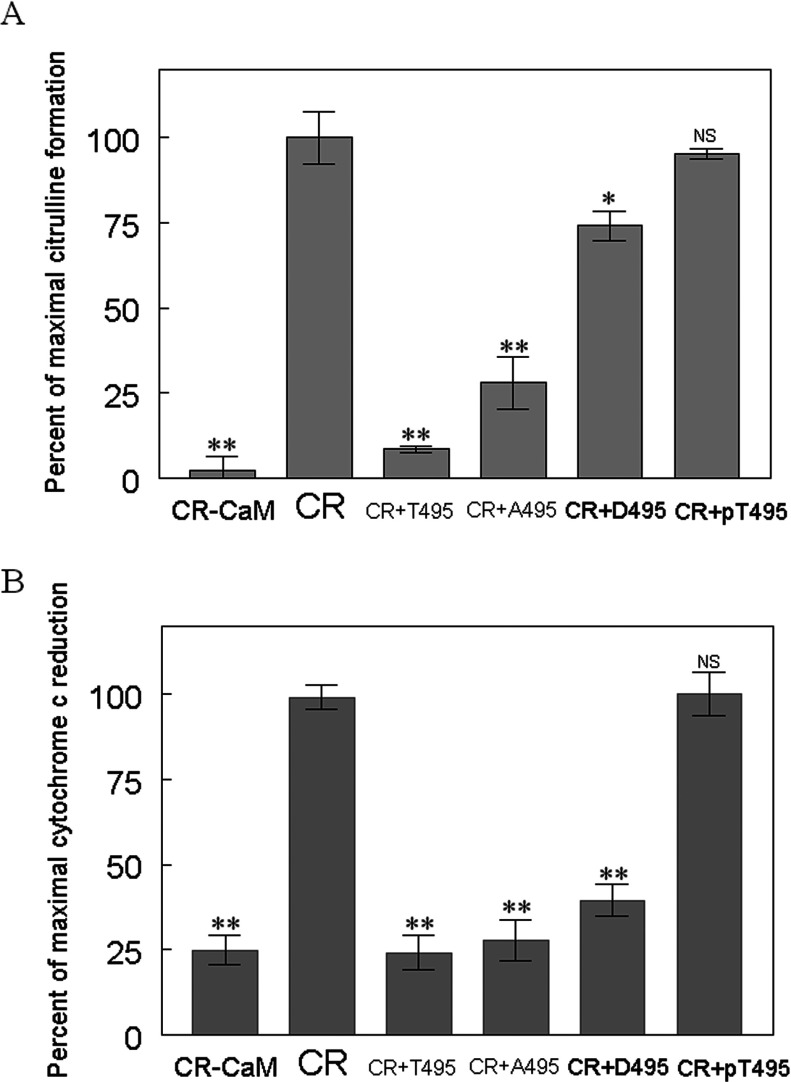
Figure 6. Evaluation of inhibitory potency of CBD variants on eNOS activity.
Modified or unmodified CBD peptides were assessed for their ability to inhibit (A) citrulline formation activity and (B) Cytochrome c reduction. CR denotes a complete reaction mixture; CR-CaM denotes omission of CaM from the complete reaction mixture; CR+T495 indicates the addition of 10 μM of unmodified CBD (T495) to the complete reaction mixture; CR+A495 denotes the addition of 10 μM of phosphonull CBD (A495) to the complete reaction mixture; CR+D495 indicates the addition of 10 μM of phosphomimetic CBD (D495) to the complete reaction mixture; CR+pT495 denotes the addition of 10 μM of phosphorylated CBD (pT495) to the complete reaction mixture. The complete reaction mixture for L-[3H]citrulline formation contains 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 0.5 μM CaM, 0.2 mM EDTA, 0.3 mM CaCl2, 100 μM β-NADPH, 10 μM H4B, 20 μM L-arginine, 1 μCi of L-[3H]arginine, 100 nM eNOS. The complete reaction mixture for cytochrome c reduction contains 25 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 50 μM cytochrome c, 0.5 μM CaM, 100 μM CaCl2 and 100 μM β-NADPH. The catalytic activity was normalized to give percentages relative to the reaction rate in the absence of each peptide. Each bar represents mean±S.D. of triplicate experiments. Under these conditions, the activities for eNOS bound to CaM were 12±2/min for citrulline formation, and 295±15/min for cytochrome c reduction. Data are presented as means±S.D.*denotes P<0.05, ** P<0.01, NS, not significant difference as compared with that in the absence of synthetic CBD peptides. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times.