Figure 1.
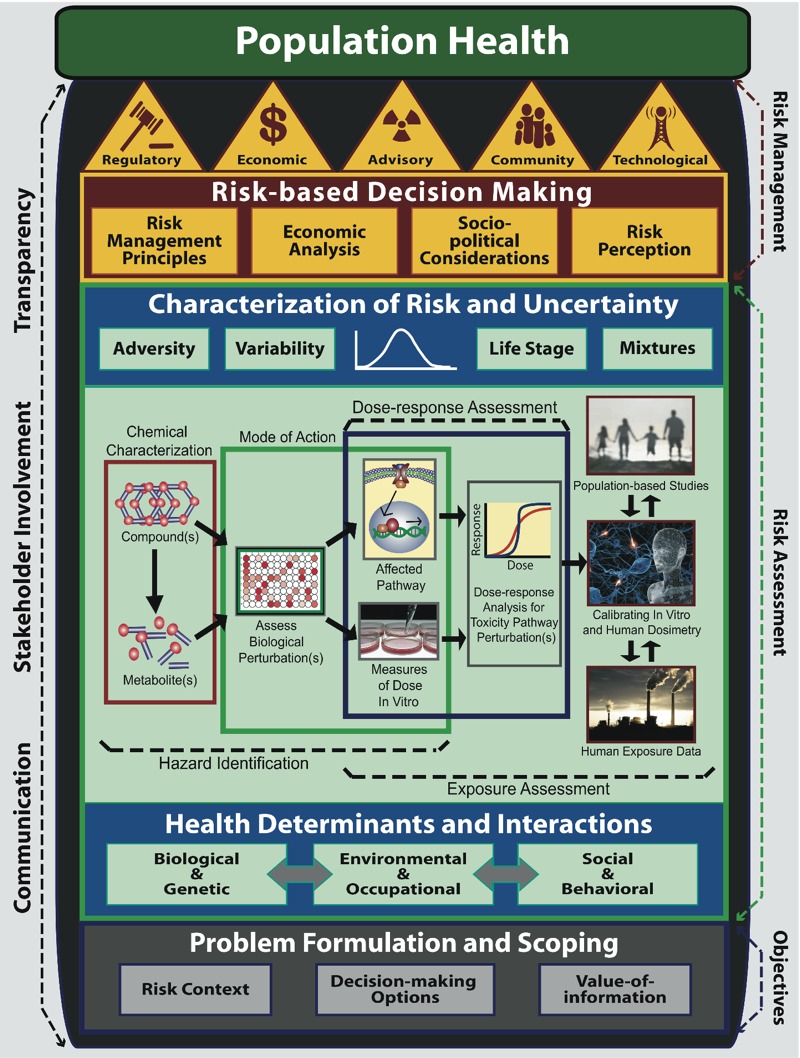
The NexGen framework for risk science. Phase I: objectives—problem formulation and scoping takes into consideration the risk context, decision-making options, and value of information. Phase II: risk assessment: health determinants and interactions—incorporates a population health approach that takes into account multiple health determinants that interact with the risk factor(s) of interest. Hazard identification, dose–response assessment, and exposure assessment make use of new scientific tools and technologies, based on high throughput screening assays and computational methods in biology and toxicology for hazard identification and dose–response assessment; in vitro to in vivo extrapolation methods for calibration of in vitro and human dosimetry; molecular and genetic epidemiology to identify toxicity pathway perturbations in population-based studies; and high-performance mass spectrometry to generate human exposure data, to assess risk. Characterization of risk and uncertainty applies new risk assessment methodologies to develop human exposure guidelines. Phase III: risk management—risk-based decision making considers fundamental risk management principles, economic analysis, sociopolitical consideration and risk perception to select one or more risk management interventions of a regulatory, economic, advisory, community-based, or technological nature for risk management. [The center section on hazard identification, dose–response assessment, and exposure assessment is adapted from Figure 2 of Krewski et al. (2011).]
