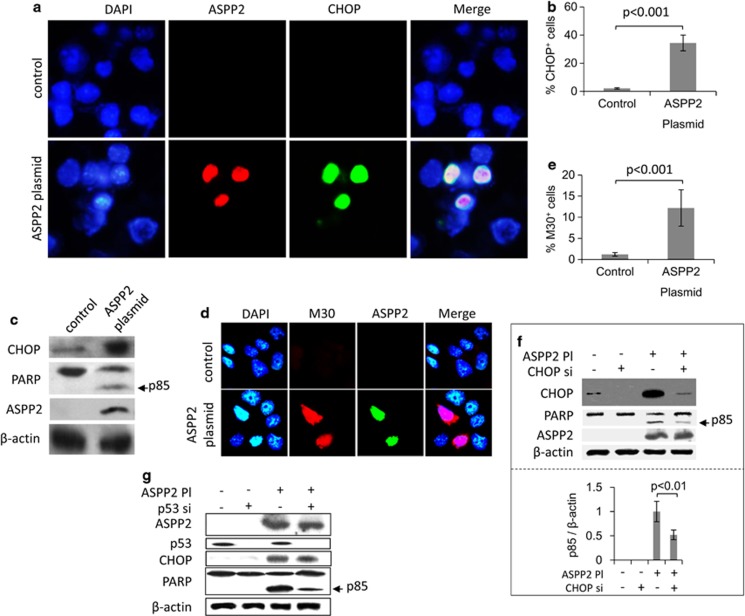
Figure 1.
ASPP2 overexpression induces p53-independent CHOP-mediated apoptosis in Hep1-6 cells. Hep1-6 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding ASPP2 (ASPP2 Pl) for 24 h. (a) Immunofluorescence detection of the expression of ASPP2 and CHOP. Nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Magnification, × 400. (b) Quantification of cells positive for CHOP expression as seen in a. Data are shown as the mean±S.E.M. of three independent experiments. (c) Immunoblot assay was used to evaluate the level of CHOP and cleaved PARP fragment (p85) in Hep1-6 cells using the indicated antibodies. (d) Immunofluorescence detection of M30-positive Hep1-6 cells. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. (e) Quantification of M30-positive cells as seen in d. Data are shown as the mean±S.E.M. of three independent experiments. (f) Immunoblot assay was used to detect the effect of CHOP knockdown via siRNA (CHOP si) on apoptosis in Hep1-6 cells using the indicated antibodies (top panel). The ratio of p85 to β-actin was calculated from densitometry scanning data. Data are shown as the mean±S.E.M. of three independent experiments (bottom panel). (g) Immunoblot assay was used to detect the effect of p53 knockdown via siRNA (p53 si) on CHOP expression and apoptosis in Hep1-6 cells using the indicated antibodies