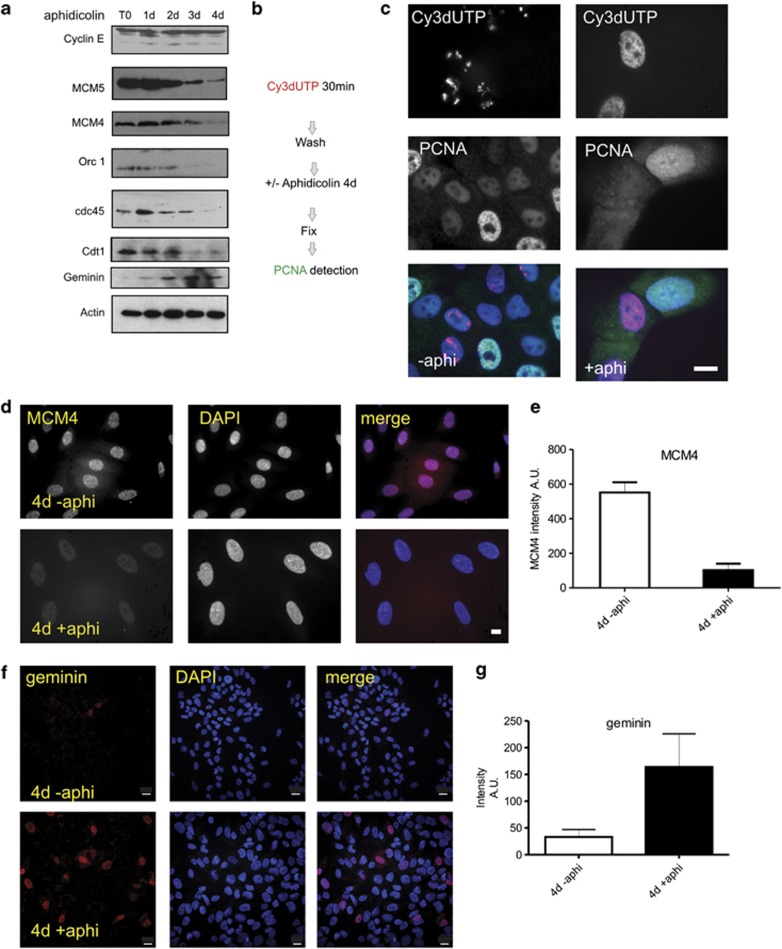
Figure 7.
Replication licensing complexes are retained during prolonged S phase arrest of MCF10A cells. The expression of proteins involved in replication control was assessed during aphidicolin-induced (1–4d) cell cycle arrest. At different times following aphidicolin treatment (days, top), selected replication proteins (left) were monitored in total extracts by immunoblotting (a). Exposures shown accentuate the general population level trends during arrest and different exposures were used to estimate fold changes at different times. For key proteins, quantitative estimates were generated using single-cell analysis (d–g). Experiments designed to test the stability of assembly of replication proteins within S phase nuclei (scheme in b) demonstrated that assembled replication foci were lost from S phase cells during prolonged arrest (c, 4 days). Prior to aphidicolin treatment, cells were pulse labelled with Cy3dUTP to mark S phase cells. Controls (no aphidicolin) showed PCNA in nuclei of cells containing pre-labelled chromosome territories. After S phase arrest (4d), cells pre-labelled with Cy3dUTP were negative for PCNA (n=500); in some experiments exposures were adjusted to improve sensitivity and this reveals background cytoplasmic staining. Nuclear retention of proteins within the replication licensing complex was assessed by immuno-staining (d–g). During prolonged arrest (4d), chromatin-associated MCM4 levels fell to 18.5% of the level in controls (d and e), based on the average fluorescence intensity of 100 nuclei after arrest (4d +aphi; AU—102.6±37.1 (S.D.); n=100) compared with control levels in untreated nuclei (4d −aphi; AU—551.78±59 (S.D.); n=100 from three independent experiments). MCM5 levels fell to 21.35% of control levels using the same approach (4d +aphi; AU—214±131.5 (S.D.); n=100. 4d −aphi, AU—1002.6+/136.46 (S.D.); n=100. Not shown). During arrest, the average geminin expression across the population increased fourfold relative to controls not treated with aphidicolin (f and g). Scale bars c, d: 10 μm; f: 20 μm