Correction to: Cell Death and Disease (2013) 4, e921; doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.448; published online 14 November 2013
Since the publication of this paper, the authors have noticed that there was an error in Figure 2a. The western blotting image was incorrect. The error has now been rectified. The corrected article appears online together with this corrigendum. The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience this may have caused.
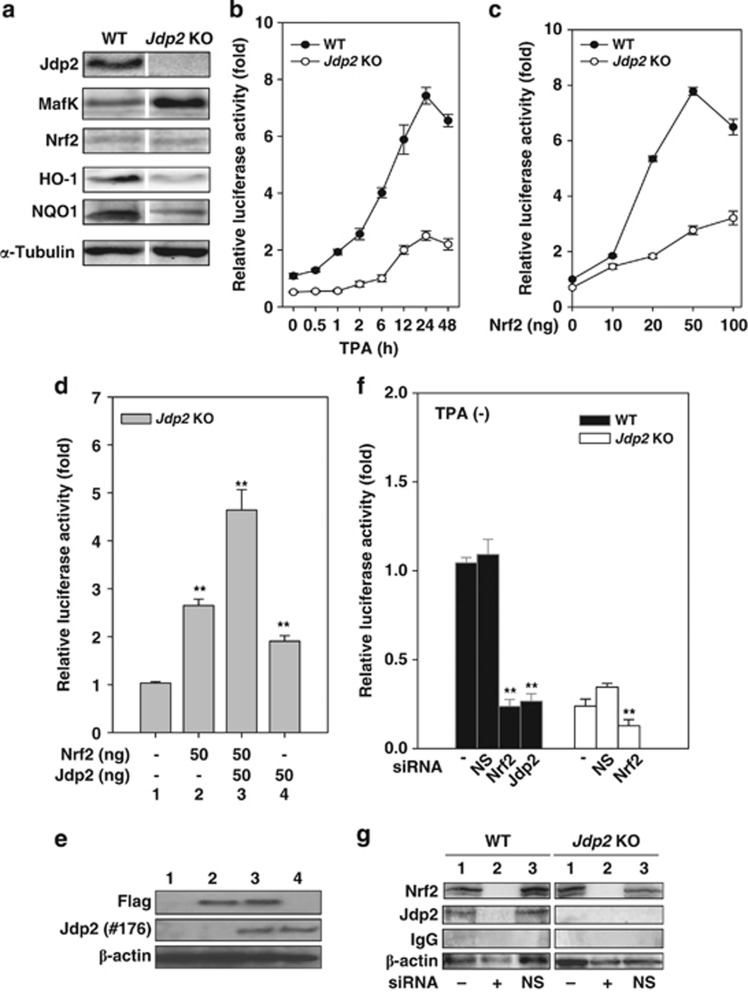
Figure 2.
JDP2 is required for ARE activation. (a) Protein detection in WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs using western blotting. The cellular lysates from WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs (40 μg) were separated on SDS-PAGE and then transferred onto a membrane. Jdp2, MafK, Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1 and α-tubulin were immunodetected using specific antibodies. (b) Relative NQO1 promoter activity in WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs in the presence of TPA at the indicated exposure times. After 24 h of culture, TPA (10–6 M) was added, transfectants with pGL4–hQR25–luciferase were incubated for an additional 48 h and luciferase activity was measured (n=3) as described in Materials and Methods. (c) Effect of Nrf2 on NQO1 promoter activity. pGL4–hQR25–luciferase (400 ng) plus 0–100 ng of pcDNA3–Nrf2 were transfected into WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs (5 × 104). One day after transfection, cells were collected and luciferase activity was measured. Values from a representative experiment are given as mean±S.D. (n=3). (d) Effect of JDP2 on ARE activity in the presence of Nrf2. Jdp2 KO MEFs (5 × 104) was transfected with 400 ng of pGL4–hQR25–luciferase, 50 ng of FLAG_S–Nrf2 and pcDNA–Jdp2, respectively, as indicated. One day after transfection, cells were collected and luciferase activity was measured (n=3). **P<0.01. (e) Protein detection of FLAG–Nrf2 and JDP2 in WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs using western blotting. The cellular lysates from WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs (40 μg) were separated on SDS-PAGE and then transferred onto a membrane. FLAG, Jdp2 and β-actin were immunodetected using specific antibodies, which were described in Materials and Methods. Lane number corresponded to each lane in d. (f) Effect of siRNA specific for Nrf2 and Jdp2 on ARE activity. WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs (5 × 104 cells) were transfected with 30 pmol of siRNA specific for Nrf2 or Jdp2 and 200 ng of pGL4–hQR25–luciferase plasmid as described in the text. After exposure for 30 h, luciferase activity was measured (n=3). The same amount of nonspecific double-stranded RNA was used as a negative control (NS). **P<0.01. (g) Inhibition of the expression of Nrf2 and Jdp2 proteins by siRNA. WT and Jdp2 KO MEFs (5 × 104) were transfected with 30 pmol of active siRNA and the control siRNA, together with reporter plasmids. After treatment for 30 h, cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using Nrf2, Jdp2, IgG or β-actin antibodies. Lane 1, without siRNA; lane 2, with siRNA; and lane 3, with NS siRNA