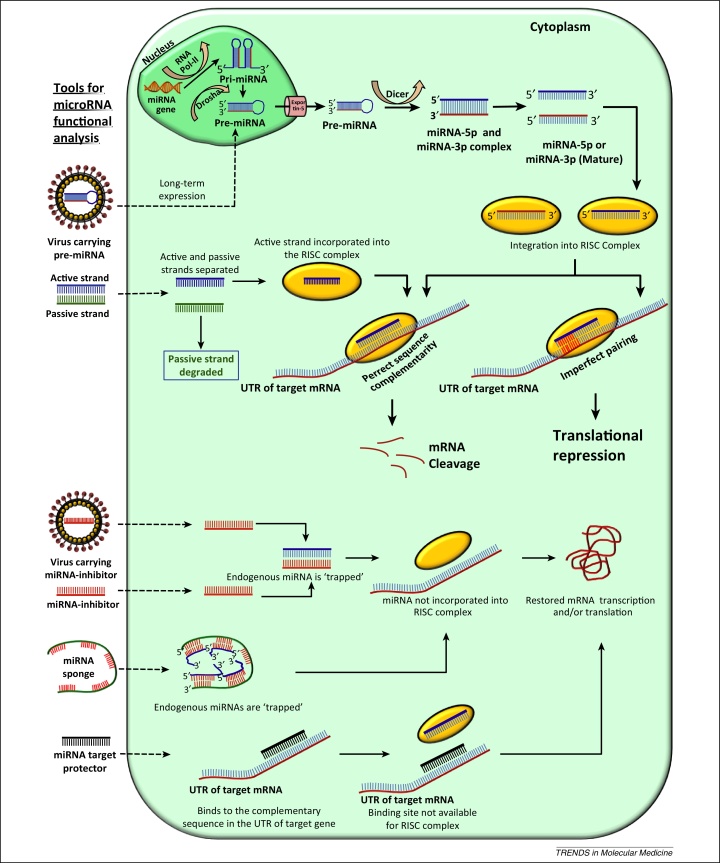
Figure 1.
miRNA biosynthetic pathway and tools available for miRNA functional analysis. Primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) transcripts are produced by RNA polymerase II (RNA pol-II) and processed by the endonuclease Drosha and its cofactors in the nucleus. The resulting hairpin-shaped precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) is transported to the cytoplasm via Exportin-5 for further processing by Dicer, an RNase-like enzyme, creating a 21-nucleotide miRNA duplex (miRNA5p–miRNA3p). The mature single-stranded miRNA is assembled into the miRNA-induced silencing effector complex (RISC). The RISC is then guided by the miRNA to complementary mRNA target sequences. Perfect sequence complementarity to the target mRNA results in mRNA degradation. Translational repression is initiated in cases of imperfect seed-region pairing. Modes of action of available tools to study miRNA-mediated functional aspects are also depicted. Lenti- or adeno-associated viral particles carrying pre-miRNA or coding sequences for either miRNA inhibitors or miRNA sponges are used to circumvent the problems of cellular uptake and to achieve long-term expression. miRNA mimics are synthetic double-stranded oligos; following cellular uptake one of the strands (the active strand) is incorporated into the RISC and directs downstream mechanisms to downregulate the mRNA target. The other strand (the passive strand) is degraded. miRNA inhibitors are single-stranded chemically modified oligonucleotides containing a sequence complementary to either the seed region or the complete sequence of the targeted miRNA. miRNA sponges are also like inhibitors but contain multiple sequences in tandem. Following cellular uptake of inhibitors or sponges, the endogenous miRNA is scavenged and cannot be incorporated into the RISC and contribute to mRNA cleavage or translational repression. miRNA target protectors work at the target mRNA level. Following cellular uptake, the target protectors bind to and block the miRNA-binding sites of the target mRNA from the RISC, ultimately resulting in bypass of RISC-associated mRNA cleavage or translational repression.