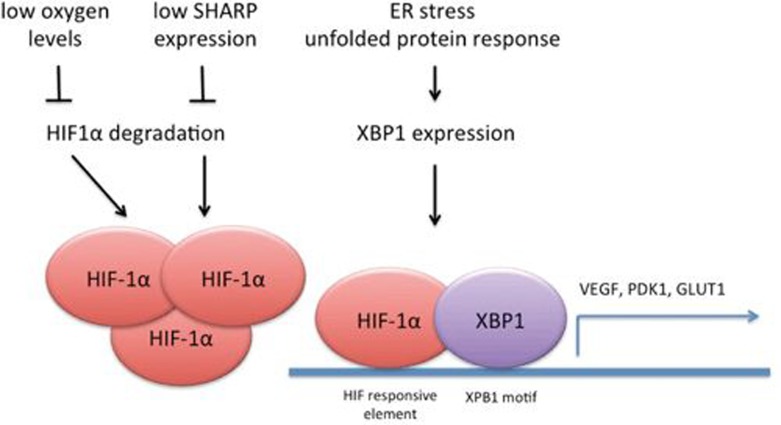
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of HIF-1α activation in TNBC. Oxygen levels regulate HIF-1α stability through hydroxylation and VHL-dependent ubiquitination, while SHARP1 regulates intrinsic HIF-1α instability, through a proteasome-dependent, ubiquitin-independent mechanism. In TNBC, local tumor hypoxia and downregulation of SHARP1 lead to increased expression of HIF-1α. In TNBC, the unfolded protein response (UPR) mediator, transcription factor XBP1, transcriptionally cooperates with HIF-1α by binding to the promoters of a number of HIF target genes and through yet unidentified mechanisms promotes HIF-1α transcriptional activity. Of note, the HRE (HIF-responsive element) and XBP1 motif in TNBC overlap6.