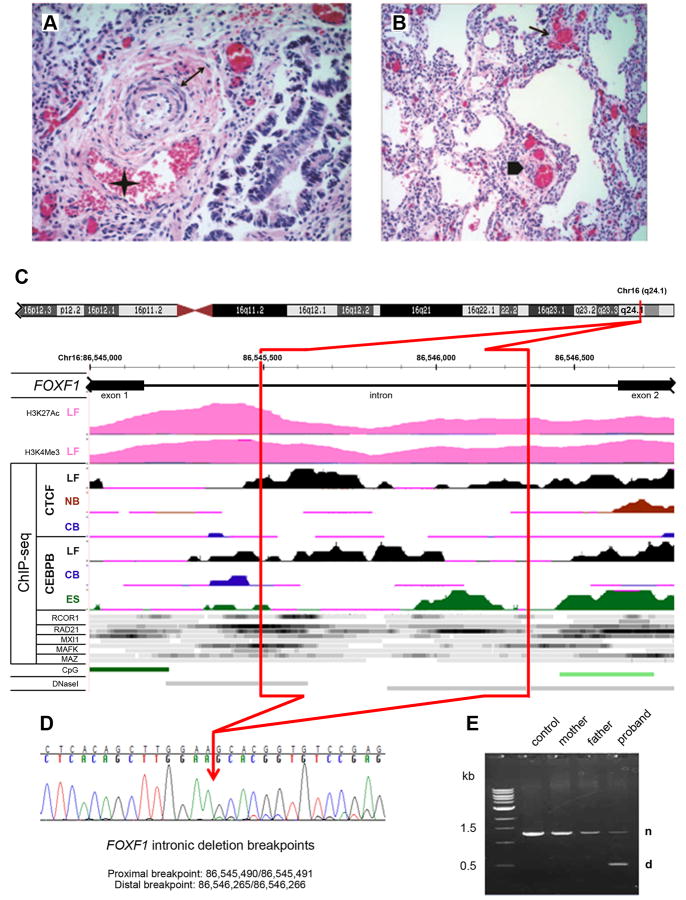
Figure 1.
Structure of the FOXF1 deep intronic deletion and the associated phenotype. A, B: Histopathology of the ACDMPV case. A: Pulmonary artery with a wall thickened by increased medial smooth muscle (double arrow) and associated with a malpositioned vein (asterisk); H&E, 40×. B: Simplified lobular architecture with paucity of capillary properly located near the alveolar epithelium, presence of dysplastic dilated capillary in the interstitium (arrow) and peripheral thickened artery accompanied by malpositioned vein (arrowhead); H&E, 20×. C: Regulatory potential of the FOXF1 intron. Deleted part of the intron is marked in red. Abbreviations: LF, normal fetal lung fibroblasts, IMR-90; NB, normal B-lymphocytes; CB, leukemia mesodermal cell line; ES, embryonic stem cells; CpG, CpG islands; DNaseI, DNaseI hypersensitive sites. ChIP-seq data for transcription regulators other than CTCF and CEBPB were obtained using LF (top ribbon) and NB cells (bottom ribbon) with the exception of RAD2 for which they were obtained from LF and ES cells. Histone modification mark for seven cell lines from ENCODE shows H3 acetylation and tri-methylation at lysine 4 in normal fetal lung fibroblasts, but not other tested cell lines. ChIP-seq signal for CTCF, CEBPB, and other transcriptional regulators (ENCODE) shows preferential interaction and/or unique pattern of interaction of these polypeptides with the FOXF1 intron in fetal lung fibroblasts. D: Chromatopherogram of the DNA sequence across the deletion breakpoints. The RefSeq transcript used was NM_001451.2 and the mutation was named as g.1358_2133del776 or g.[1_1357del;2134_3938del], following the standard human sequence variant nomenclature using Mutalyzer program (http://www.lovd.nl/mutalyzer/). E: PCR amplification of the normal (n) and truncated (d) copies of the FOXF1 intron from genomic DNA.