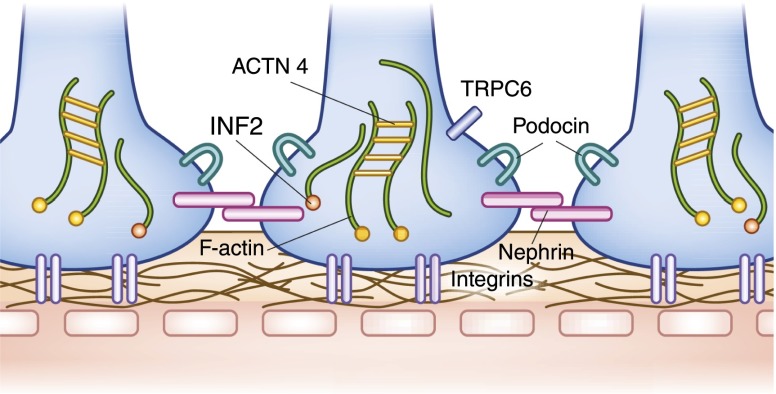
Figure 5.
Major molecular components of the podocyte and slit diaphragm. Interdigitating podocytes from neighboring cells form the elaborate slit diaphragm that is composed of nephrin. Podocin helps regulate trafficking of nephrin to the slit diaphragm. Proteins α-actinin-4 and INF2 play important roles in the maintenance of the actin cytoskeleton, whereas integrins help anchor the podocytes to the glomerular basement membrane. Mutations in α-actinin-4, INF2, and TRPC6 channel all cause autosomal dominant forms of FSGS. Mutations in nephrin and podocin cause recessive forms of steroid-resistant nephrosis.