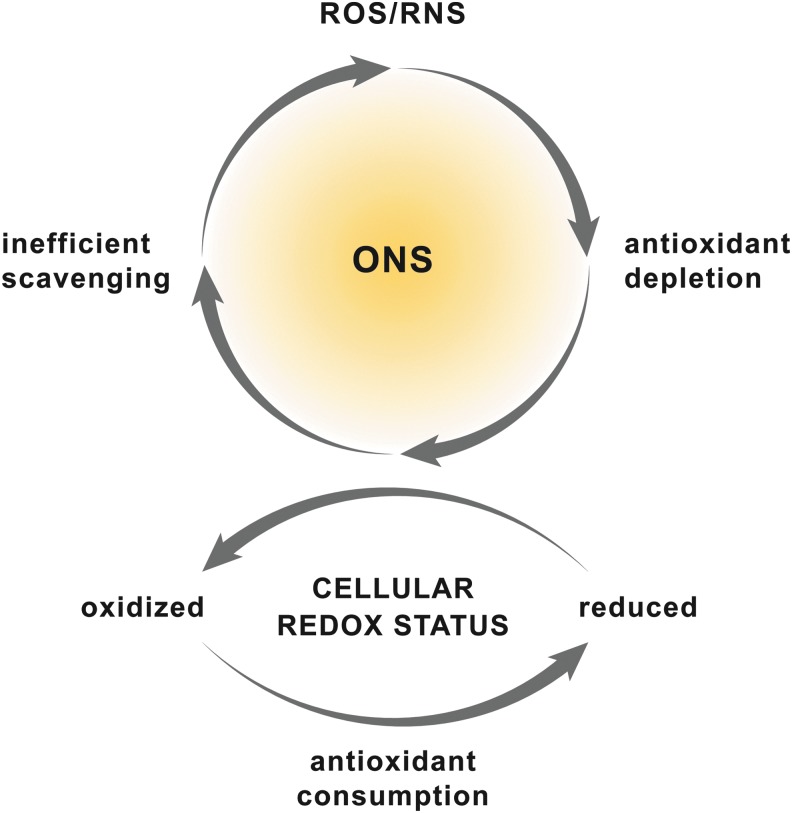
FIG. 1.
Etiology of ONS. ONS is the result of a disrupted balance between intracellular levels of ROS/RNS and antioxidants. The production of large amounts of ROS/RNS consumes cellular antioxidants, which leads to inefficient ROS/RNS scavenging and hence ONS (upper panel). Simultaneously, the cellular redox status shifts toward a more oxidized state. Alternatively, disruption of the cellular redox status can induce ONS because of the consequent consumption and depletion of cellular antioxidants (bottom panel). ONS, oxidative/nitrosative stress; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars