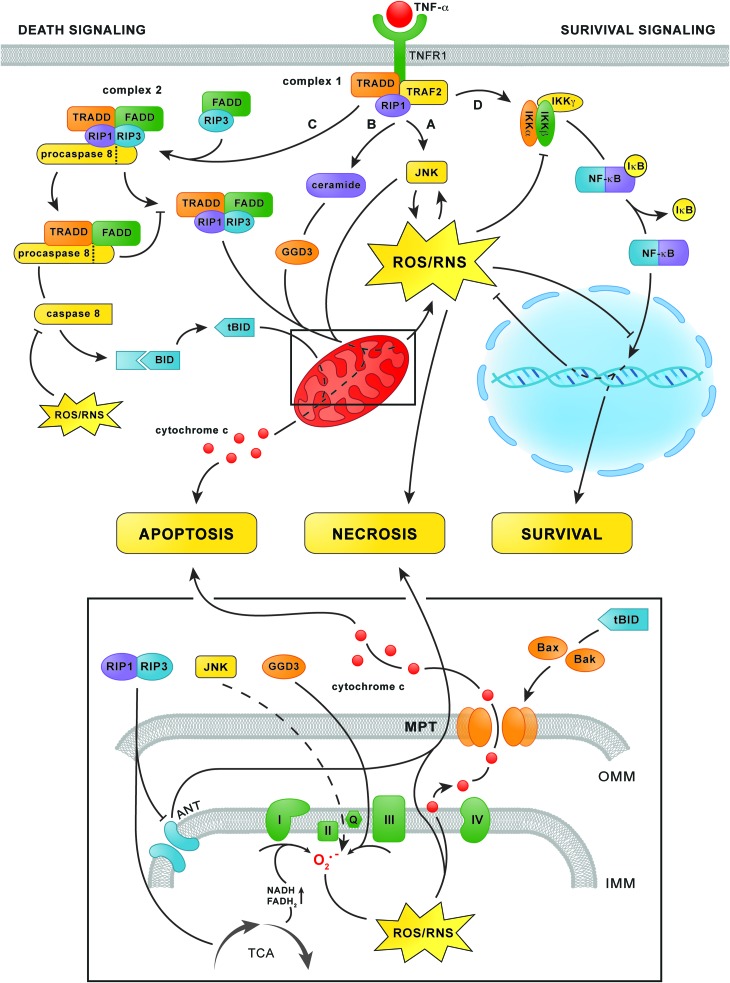
FIG. 7.
TNF-α signaling in hepatocytes. After TNF-α binding to TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, and RIP1 are assembled at the cytosolic domain of TNFR1 to form complex 1 (top center). Complex 1 subsequently initiates two branches of the trinomial death signaling cascade via the phosphorylation of JNK (pathway A) as well as the accumulation of ceramide and the subsequent increase in GGD3 synthesis (pathway B). Both routes increase mitochondrial O2•− formation (bottom panel), although the exact mechanism of JNK-mediated O2•− formation remains elusive (dashed line). The formation of derivative ROS/RNS from O2•− and corollary activation of cytochrome c peroxidase activity subsequently leads to the dissociation of cytochrome c from the IMM (bottom panel), a prerequisite for apoptosis. In addition, sustained JNK-dependent ROS/RNS formation leads to MPT and necrosis. Simultaneously, complex 1 triggers survival signaling via activation of the IKK complex (pathway D, top right), which phosphorylates IκB-α. This enables the dissociation of IκB-α from NF-κB and its translocation to the nucleus to initiate the transcription of anti-apoptotic and antioxidative genes. At a later time point, TRADD and RIP1 dissociate from complex 1 and associate with FADD, procaspase 8, and RIP3 to form complex 2 (upper left corner). Complex 2 mediates the third branch of the death signaling cascade (pathway C) by activating caspase 8, which subsequently truncates Bid into tBid. Thereafter, tBid induces permeabilization of the OMM via the accumulation of Bax and Bak, which enables the release of cytochrome c into the cytosol (bottom panel and top left) and consequent induction of apoptosis. When caspase 8 is inhibited as a result of oxidation, the RIP1/RIP3 complex (top left) fuels mitochondrial ROS/RNS production via upregulation of the TCA cycle and inhibition of the ANT in the IMM (bottom panel), which eventually leads to MPT and necrosis. ANT, adenine nucleotide translocator; FADD, Fas-associated protein with death domain; GGD3, ganglioside GD3; IKK, IκB kinase; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; IκB-α, nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor α; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MPT, mitochondrial permeability transition; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; RIP1/3, receptor-interacting kinase 1/3; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; TNFR1, TNF-α receptor-1; TRAF2, TNF-α receptor-associated factor 2. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars