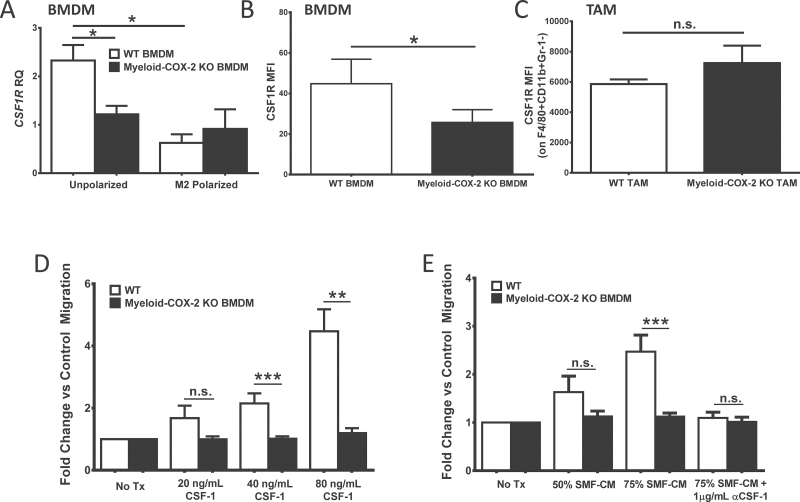
Fig. 4.
Deletion of myeloid cell COX-2 reduces macrophage CSF-1R expression and migration. (A) CSF-1R expression was lower in naive myeloid-COX-2 KO BMDM compared with WT by Q-PCR for mRNA. M2 polarization (20ng/ml IL-4 and 10ng/ml IL-13, 18h) reduced CSF-1R expression in WT BMDM but did not further modify levels in myeloid-COX-2 KO (n = 6). (B) By flow cytometry, CSF-1R surface expression was reduced in myeloid-COX-2 KO BMDM compared with WT (n = 4) although (C) TAM surface CSF-1R expression was not different between genotypes (n = 3–4). Migration of myeloid-COX-2 KO BMDM was significantly reduced compared with WT BMDM toward (D) CSF-1 or (E) conditioned medium from SMF tumors cells (SMF-CM, n = 5–10). Addition of CSF-1 neutralizing antibody (αCSF-1) ablated WT BMDM migration toward SMF-CM (n = 3). MFI = mean fluorescence intensity; RQ = relative quantity. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. = not significant.