Fig. 1.
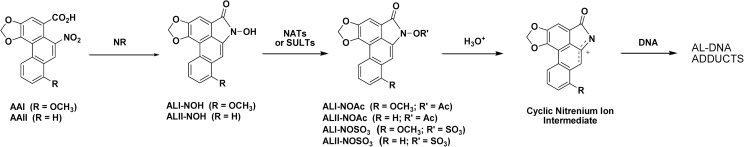
Proposed route for bioactivation of AAs. AA-I and AA-II undergo four electron nitroreduction to form AL-I-NOH and AL-II-NOH followed by N-acetylation or N-O-sulfonation catalyzed by NATs and SULTs, respectively. AL-N-oxyesters (AL-I-N-OAc, AL-II-N-OAc, AL-I-N-OSO3H and AL-II-N-OSO3H) solvolize in aqueous solution, leading to cyclic nitrenium ion formation, which, in turn, reacts with DNA to form AL-DNA adducts.
