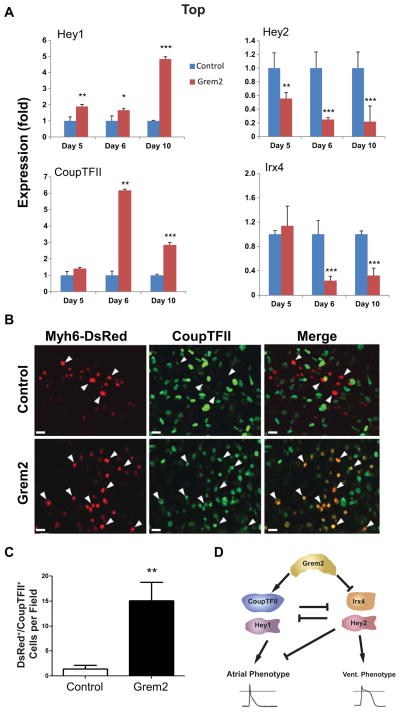
Figure 5. Grem2 induces atrial and suppresses ventricular specific transcriptional regulators.
CGR8 ES cells were allowed to differentiate untreated (Control) or treated with Grem2 between differentiation days 4–10. (A) Quantitative PCR analysis of RNA samples isolated at day 5, 6, and 10 of differentiation shows induction of Hey1 and CoupTFII and suppression of Hey2 and Irx4 after Grem2 treatment. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001, comparing Grem2 samples to Controls of the same time point, which were arbitrarily set at value 1. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of EBs generated using ES cells engineered with the Myh6-DsRed construct and stained with an antibody recognizing CoupTFII at day 12 of differentiation. Grem2-treated cultures contain cardiomyocytes (red nuclear fluorescence) that express nuclear CoupTFII in green (arrowheads), whereas Control cultures display fewer CoupTFII+ cardiomyocytes. Scale bar is 10 μm. (C) Quantification of immunofluorescence in panel B shows 11-fold increase in DsRED/CoupTFII double positive cardiomyocytes by Grem2. ** P < 0.01. (D) Schematic model of Grem2 effects on cardiomyocyte differentiation. CoupTFII and Hey 1 promote atrial differentiation, whereas Hey2 and Irx4 enhance ventricular and suppress atrial differentiation. Grem2 directly or indirectly induces CoupTFII and Hey1, and blocks Irx4 and Hey2 expression. The net result is an increase of atrial differentiation.