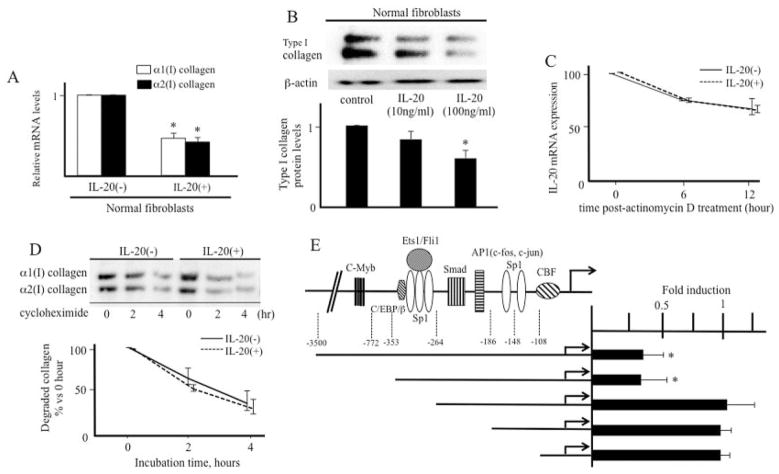
Figure 1.
Effect of interleukin-20 (IL-20) on collagen expression. A, Normal fibroblasts were treated with IL-20 (100 ng/ml) for 12 hours. Levels of collagen mRNA were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (n = 7 samples). ⅞* = P < 0.05 versus untreated fibroblasts (set to 1.0). B, Normal fibroblasts were treated with IL-20 (100 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting. The protein levels of type I collagen quantitated by scanning densitometry and corrected for the levels of β-actin in the same samples are shown relative to those in untreated fibroblasts (set to 1.0) (n = 3 samples). * = P < 0.05 versus untreated fibroblasts. C, Fibroblasts were incubated in the presence or absence of IL-20 for 12 hours before the addition of 2.5 μg/ml actinomycin D for 6 or 12 hours. IL-20 mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time PCR. D, Fibroblasts were incubated in the presence or absence of IL-20 for 24 hours before the addition of cycloheximide (10 μg/ml). Cells were harvested at the indicated time points after cycloheximide was administered, and immunoblotting was performed. The protein levels of type I collagen quantitated by scanning densitometry and corrected for the levels of β-actin in the same samples are shown relative to those in untreated fibroblasts (set to 1.0) (n = 3 samples). E, The indicated α2(I) collagen promoter deletion constructs were transfected into normal fibroblasts in the absence or presence of IL-20 (100 ng/ml) for 24 hours (n = 3 samples). The bar graph represents fold stimulation of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activities stimulated with IL-20 relative to those not stimulated with IL-20 (set to 1.0). * = P < 0.05 versus cells not stimulated with IL-20. Values are the mean ± SEM. c/EBPβ = CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β; AP-1 = activator protein 1; CBF = CCAAT-binding transcription factor.