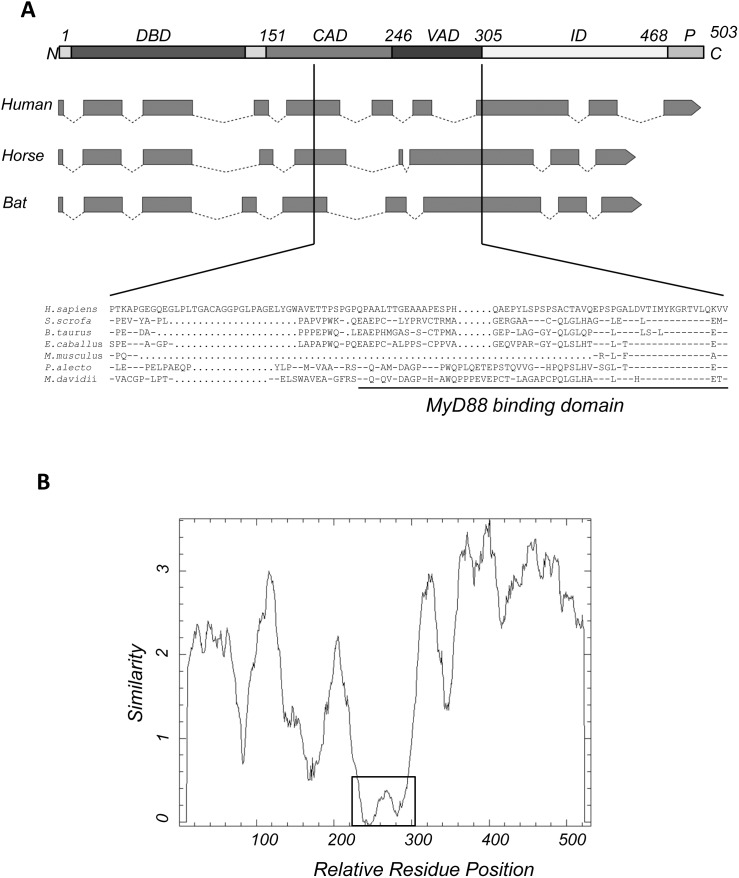
Figure 1. Comparison of bat IRF7 with IRF7 from other species.
(A) Functional domains of IRF7 were drawn (top) based on human IRF7 [37]. The intron-exon structure of IRF7 from human, horse and bat were predicted by alignment of individual ORFs to their respective genomes. Solid boxes indicate exons while dotted lines represent introns; arrows mark the direction and the end of the genome structure. The deduced protein sequence of the region corresponding to human MyD88 binding motif (aa 247–305) from seven species including human, pig, cow, mouse, horse, P. alecto bat and M. davidii bat was aligned. DBD: DNA binding domain; CAD: constitutive activation domain; VAD: virus-activated domain; ID: autoinhibitory domain; P: phosphorylation sites, serine-rich domain. Dashes indicate similarity; dots indicate gaps. (B) Sequence similarity plot of P. alecto IRF7 with IRF7 from human, mouse, cow, pig, horse and M. davidii using a 20 amino acid sliding window and created using EMBOSS Plotcon (http://emboss.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/emboss/plotcon). The similarity across the whole ORF between these species is shown by scores. The lower the score the lower the sequence conservation. The least conserved region is boxed.