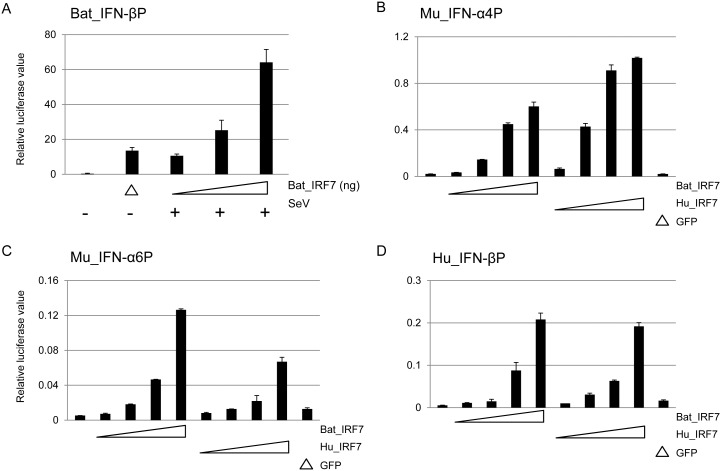
Figure 3. IFN-β is induced in a dose-dependent manner by bat IRF7.
(A) Sendai virus (SeV) induced higher IFN-β induction with an increasing dose of bat IRF7. Bat PaKiT03 cells (2×105 per well) were cotransfected with 0, 10, 50 or 100 ng pCAGGS-bat IRF7 (left to right, last three bars) and bat IFN-β promoter plasmid. 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected with 100 HAU SeV per well or mock infected (left to right, first two bars, Δ indicates transfection with 100 ng pCAGGS-bat IRF7) followed by promoter activation assay six hours after infection. Values show the mean of two experiments and error bars indicate standard errors. (B–D) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with 0, 1, 10, 100 or 500 ng of expression plasmids for either bat (left to right, first five bars) or human IRF7-GFP (next four bars) with mouse IFN-α4 (B) IFN-α6 (C) or human IFN-β (D) promoter plasmid. GFP expression plasmid was used at 500 ng per well as negative control. After 30 h, cells were analysed for promoter activity by reporter gene assay. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. Values show the average of two experiments and error bars indicate standard errors.