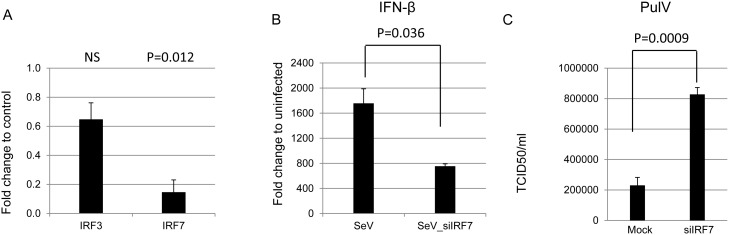
Figure 4. siRNA knockdown of bat IRF7 reduces IFN production and increases viral replication.
(A) siRNA knock down of bat IRF7 in bat PaKiT03 cells. Cells were transfected with a final concentration of 20 nM of siIRF7 and collected 24 hrs later for qRT-PCR analysis of IFN-β mRNA. Knock down of bat IRF7 mRNA was compared with IRF3 which served as an indication of off-target effects. (B) Knockdown of bat IRF7 significantly reduced IFN-β mRNA induction by SeV. Cells were transfected with 20 nM siIRF7 for 24 h followed by infection with SeV for a further 6 h and then collected for qRT-PCR analysis. IFN-β mRNA following SeV or SeV plus siIRF7 was measured. Results represent the mean of triplicate samples. Error bar represent the standard error. The p-values were determined relative to control untransfected cells using two sample t-tests assuming unequal variances. NS, not significant. (C) Bat PulV grows to a high titre in bat IRF7-silenced PaKiT03 cells. Cells were transfected with or without 20 nM siIRF7 and then 24 h later infected with PulV at a moi 10 for a further 24 h. Virus containing supernatant was tested for PulV titre by TCID50. Experiments were performed in triplicate and results indicate mean values. Error bar represent standard error. The p-values were determined using two sample t-tests assuming unequal variances.