Figure 1.
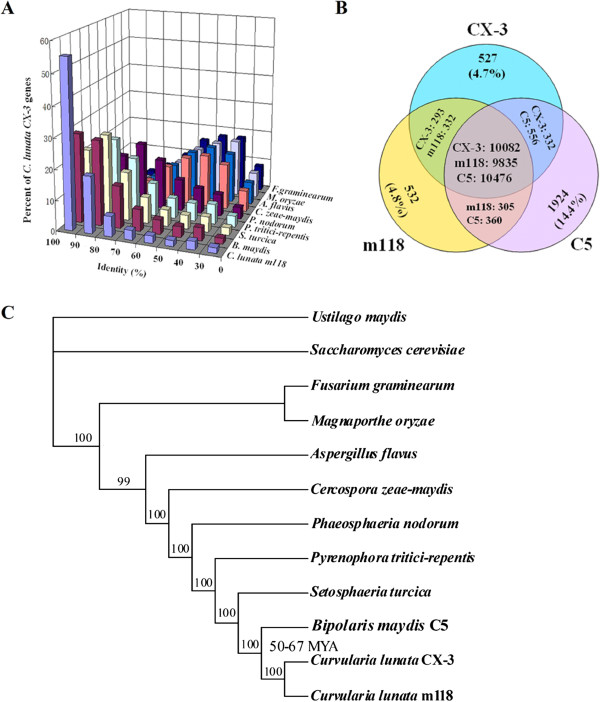
Comparative genomics and evolutionary analysis of C. lunata. (A) Amino acid sequence identity of C. lunata CX-3 with other fungi. (B) Reciprocal Blast analysis of the protein sequences among the three pathogenic fungi C. lunata CX-3, C. lunata m118 and B. maydis C5 with a cut-off E value of 1e-5. CX-3, C. lunata CX-3; m118, C. lunata m118; C5, B. maydis C5. In relative to B. maydis C5, C. lunata CX-3 and C. lunata m118 have 820 (7.3%) and 864 (7.9%) species-specific genes; In relative to C. lunata, B. maydis C5 has 1924 (14.4%) species-specific genes. C. lunata CX-3 and C. lunata m118 have 859 and 837 strains-specific genes, respectively. (C) A phylogenetic tree constructed with the Dayhoff amino acid substitution model representing the evolutionary relationships of C. lunata and other fungi. MYA, million years ago. B. maydis = C. heterostrophus.
