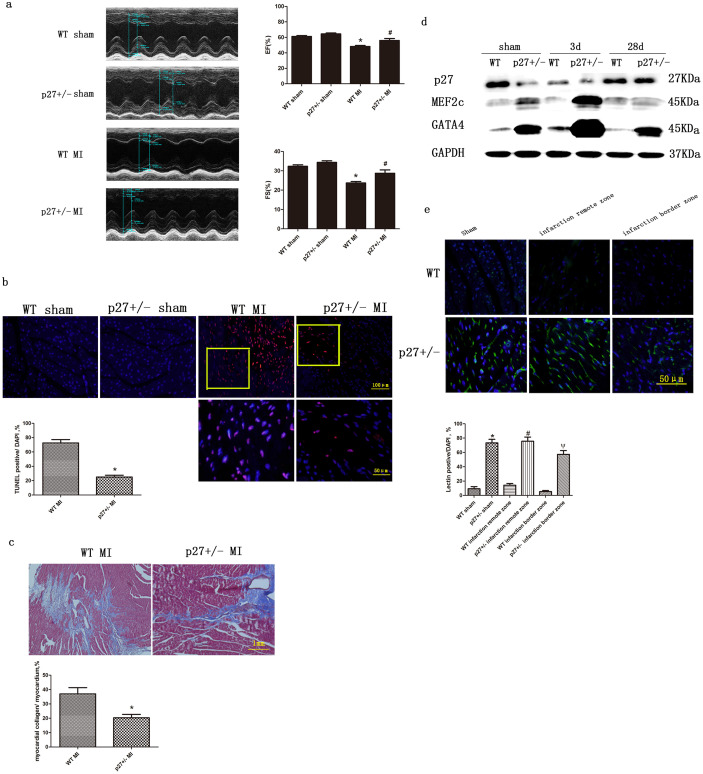
Figure 1. The effect of p27kip1 haplo-insufficiency on post-infarction cardiac function, remodeling, injury and angiogenesis.
(a) Representative M-mode echocardiograms from WT and p27+/− mice at 28 days after sham or myocardial infarction (MI) operations, groups of echocardiographic data ((n = 10 echocardiograms per echocardiographic group). *P < 0.05 versus sham; #p < 0.05 versus WT+MI. (b) Representative photomicrographs of TUNEL-positive cells (red) and nuclei (blue) in sections from sham or MI hearts. The lower panel is the enlarged box for WT+MI or p27+/− + MI. Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells in mouse hearts. * p < 0.05 compared with the WT + MI group. (c) Representative photomicrographs of MI hearts stained using Masson trichrome. The scar area was larger in WT mice than in p27+/− mice. * p < 0.05 compared with the WT MI group. (d) Representative immunoblots of MEF2c and GATA4 in the LV of p27+/− or WT mice at 3 and 28 days after a sham or MI operation. GAPDH served as the loading control. (e) Representative photomicrographs of IB4 lectin-positive cells (green) and nuclei (blue) in hearts after sham or MI operations. Quantitative analysis of IB4 lectin-positive cells, *p < 0.05 versus WT sham; #p < 0.05 versus WT infarction remote zone; ψp < 0.05 versus WT infarction border zone (n = 3).