Fig. 2. Reporter assay analysis identifies possible promoter region of P. falciparum maebl.
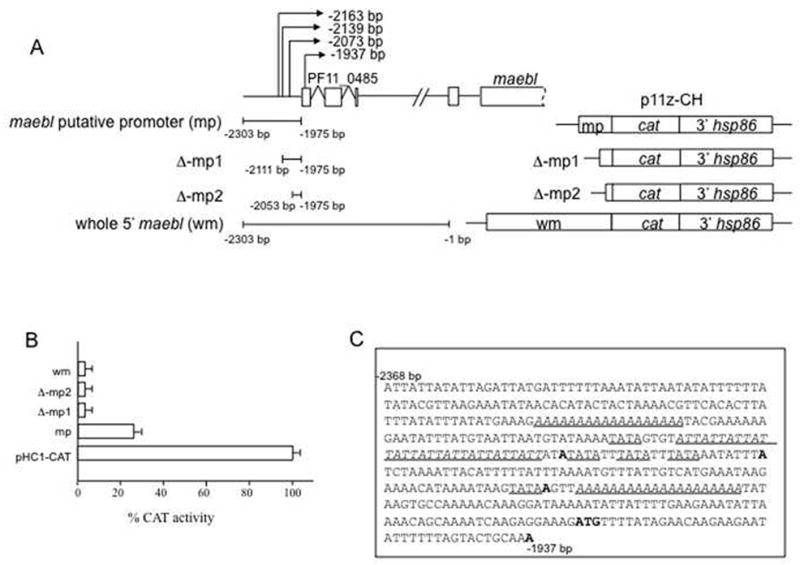
A. Two different regions from 5′ maebl were first tested for promoter activity. maebl putative promoter (mp) consisted of a 329 bp region upstream of PF11_0485. Whole 5′ maebl (wm) contained mp along with the rest of the 5′ UTR of maebl. The two maebl 5′ regions were cloned individually into a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) reporter plasmid, p11z-CH, created for transient assays in P. falciparum. Unidirectional exonuclease deletions on mp resulted in Δ-mp1 and Δ-mp2. B. Forty eight hours post-transfection, the parasite cell lysate was assayed for CAT expression. CAT activity was compared to the control plasmid pHC1-CAT that contained a strong, constitutive calmodulin promoter. The 5′ region ‘mp’ around the transcription start sites showed significant promoter activity that was greatly reduced in the deletions Δ-mp1, Δ-mp2. The 5′ region ‘wm’ also displayed only slightly detectable promoter activity. C. Sequences around the transcription start sites show the possible cis regulatory motifs in 5′ maebl (italicized and underlined). Homopolymeric (dA) tracts are seen along with (ATT)10 trinucleotide repeats, which are known to cause structural changes in the DNA. Some TATA boxes are also seen around the start sites. Shown in bold are the four transcription start sites mapped for maebl and the start codon of PF11_0485.
