Figure 2.
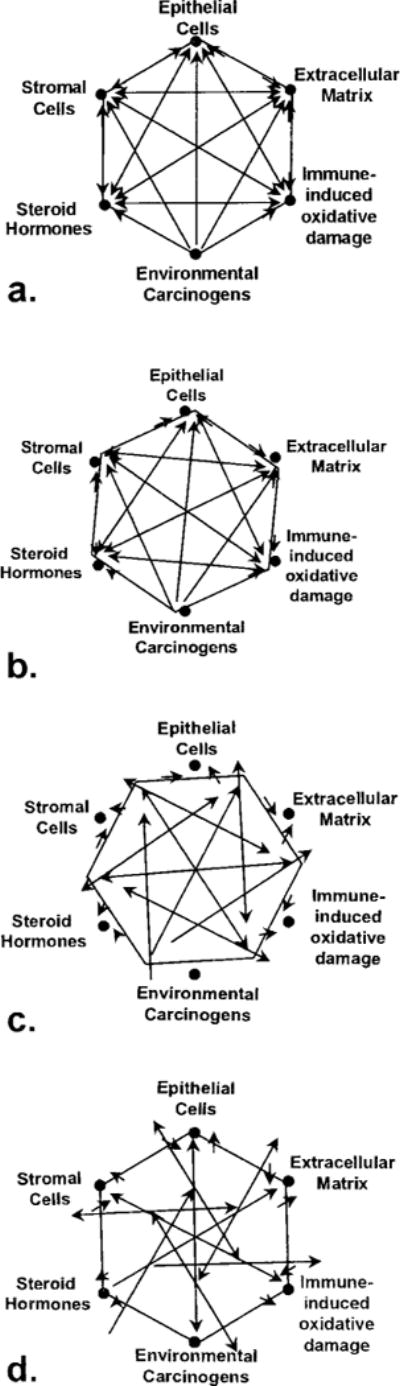
Representation of inter-relationships within the prostatic microenvironment. The interplay between epithelial cells, stromal cells, ECM, steroid hormones, oxidative damage and carcinogens contribute to the homeostasis of tissue function (a). Dysequilibrium within the tissue results from initial insults even within one component (b) and causes minor imbalance of regulation (arrows) between the rest of components. Additional insults (c and d) in the same or additional components lead to increasingly chaotic state with loss of regulation of growth and function within the tissue.
