Figure 2.
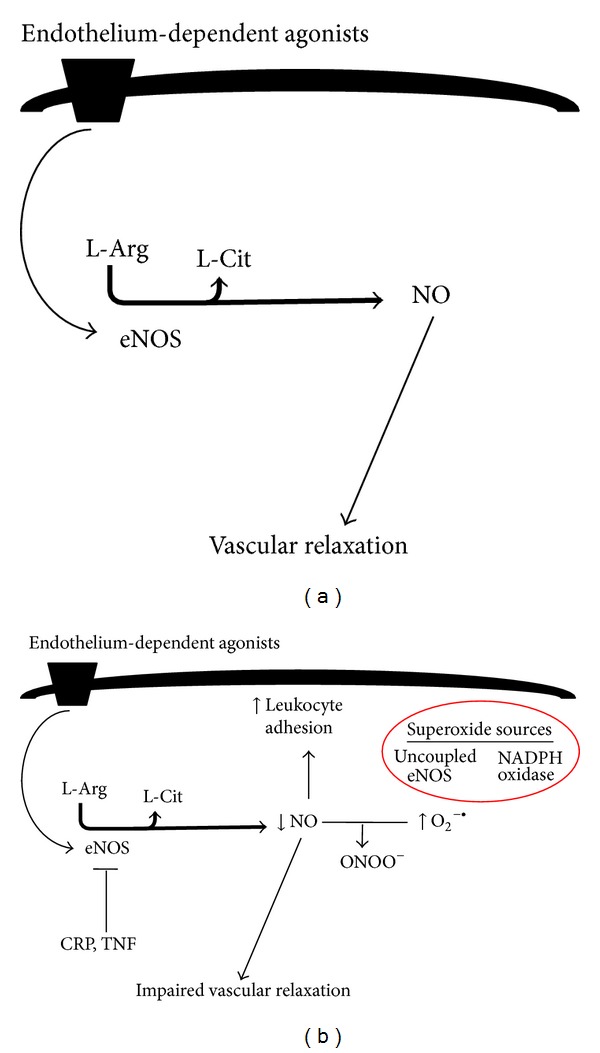
(a) Diagram illustrating endothelium-dependent relaxation during health. (b) Diagram illustrating mechanism by which inflammation and oxidative stress cause endothelial dysfunction. Inflammatory mediators such as CRP and TNF destabilise eNOS mRNA (thus inhibiting eNOS). NO protects endothelium by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion; thus, impaired NO function results in increased leukocyte adhesion. Increased superoxide (derived from NADPH oxidase or uncoupled eNOS) impairs NO bioavailability and leads to impaired vascular relaxation. The figure is based on text.
