Figure 2.
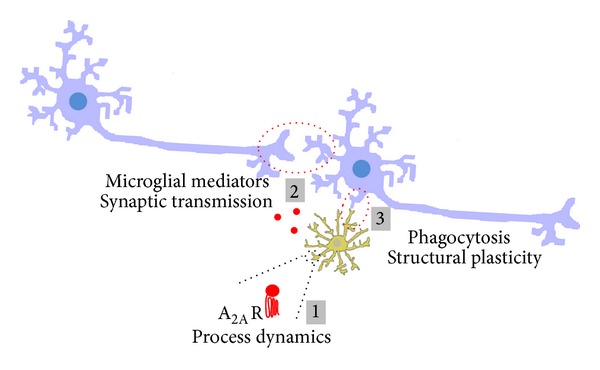
Microglia in the healthy brain/retina. Schematic representation of the main functions exerted by microglia (in yellow) under physiological conditions: surveying the environment by constant extension and retraction of processes (it remains to clarify if A2AR regulate this process, as occurs in pathology) (1); regulation of basal synaptic transmission and plasticity through the release of mediators (red circles), some of them being also important mediators of inflammation (2); regulation of spine/synapse structural plasticity, mainly by phagocytosis, a process regulated by inflammatory mediators, according to the neuronal workload (3).
