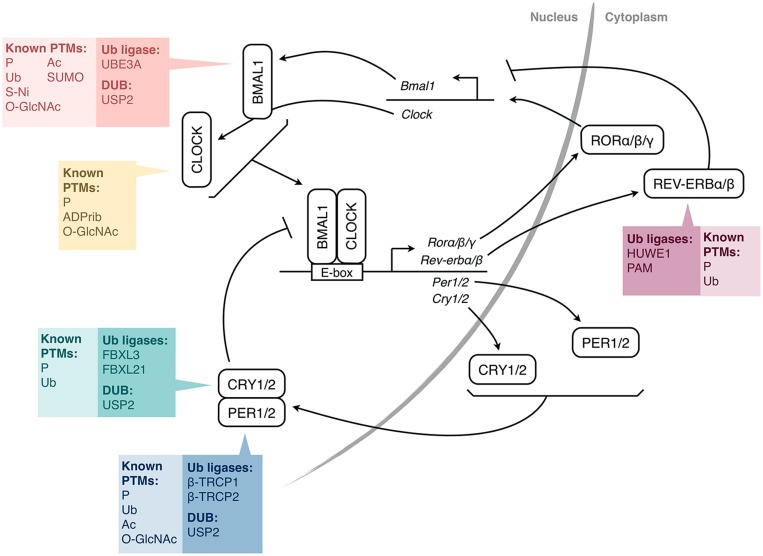
FIGURE 1.
Simplified molecular mechanism of the mammalian circadian clock. The transcription factors CLOCK and BMAL1 activate the expression of Per and Cry genes through E-box elements in their promoters. PER and CRY proteins form complexes and feedback negatively on CLOCK/BMAL1 activity, and thus, on their own expression. CLOCK/BMAL1 also activate genes encoding nuclear receptors of the REV-ERB and ROR families, which regulate the expression of Bmal1 (and also Cry1 and Clock). For each protein or pair of proteins, the colored boxes list the post-translational modifications (PTMs) that have been identified so far, as well as the ubiquitin-modifying enzymes shown to be involved (HUWE1, PAM, β-TRCP1/2 are also called ARF-BP1, MYCBP2, FBW1A/B, respectively). For simplicity, a single box per protein is shown, irrespective of the subcellular localization of the PTMs. P, phosphorylation; Ub, ubiquitination; Ac, acetylation; SUMO, SUMOylation; O-GlcNAc, addition of β-D-N-acetylglucosamine; S-Ni, S-nitrosylation; ADPrib, ADP-ribosylation; PER, Period; CRY, Cryptochrome; ROR, Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor; DUB, deubiquitinating enzyme.