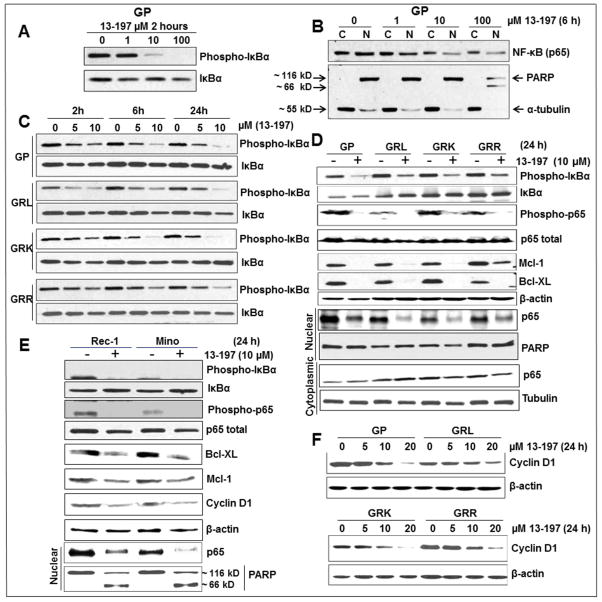
Figure 3. Effect of 13-197 on the NF-kB pathway associated molecules in therapy-resistant MCL cells.
MCL cells were cultured in RF-10 media containing vehicle (DMSO) or indicated concentration of 13-197 for different time points. After incubation, cells were harvested and whole cell lysate or cytoplasmic/nuclear fraction was prepared and subjected to western blot for the expression of NF-kB pathway associated proteins. A: shows the levels of IkBα phosphorylation by 13-197 in GP cells in a dose-dependent manner; B: shows the decrease levels of NF-kB nuclear translocation in GP MCL cells following treatment with different concentrations of 13-197. PARP and α-tubulin were also detected to confirm cytoplasmic and nuclear fractionation of proteins; C: phosphorylation status of IkBα by 13-197 in therapy-resistant and their parental GP cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner; D: status of IkBα and p65 phosphorylations, p65 nuclear translocation, Mcl-1 and Bcl-XL in therapy-resistant and their parental GP cells following treatment with 10 μM 13-197; E: levels of IkBα and p65 phosphorylations, p65 nuclear translocation, Mcl-1, Bcl-XL and cyclin D1 in Rec-1 and Mino MCL cell lines following treatment with 10 μM 13-197; F: expression levels of cyclin D1 in therapy-resistant and parental GP cell lines following treatment with different concentrations of 13-197. β-actin was used as an internal control in all these experiments. The results shown are a representative of three sets of independent experiments.