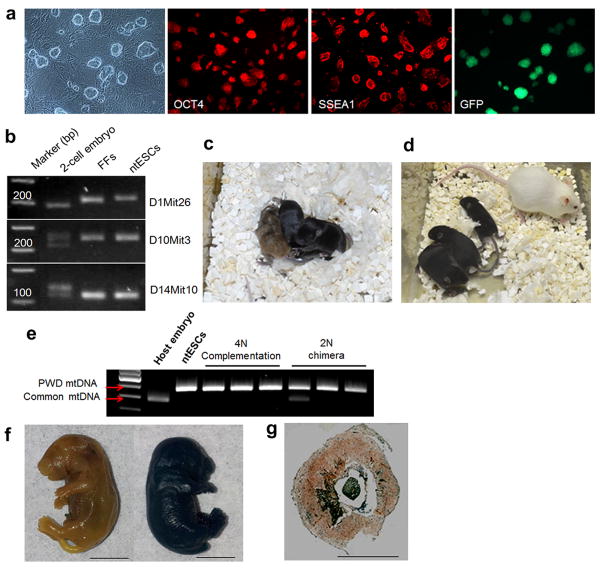
Figure 3. Characterization of ntESCs and live offspring born after interphase SCNT.
a, Morphology of ntESCs and expression of the pluripotency markers Oct4 and SSEA1 by immunostaining. Far right; re-expression of GFP in ntESCs derived from fetal fibroblasts carrying Oct4/GFP. b, Genotyping of ntESCs using chromosomal markers D1Mit26, D10Mit3 and D14Mit10. c, 2N chimeric pups generated by injection of ntESCs from cumulus cells (black) into ICR host embryos (albino). Note that two of the three pups contained exclusively ntESC phenotype. d, 4N complementation pups produced after injection of ntESCs (black) into tetraploid host embryo (agouti). e, Genotyping of chimeric offspring generated with ntESCs derived from cumulus cells by mtDNA profiling. All tetraploid and two of the three 2N chimeras contained ntESC mtDNA only. f, X-gal staining of control (non-stained, left) and cloned pup carrying LacZ gene (blue stained, right). g, X-gal detection of placental tissue section in cloned pups. Bar = 0.5 cm.