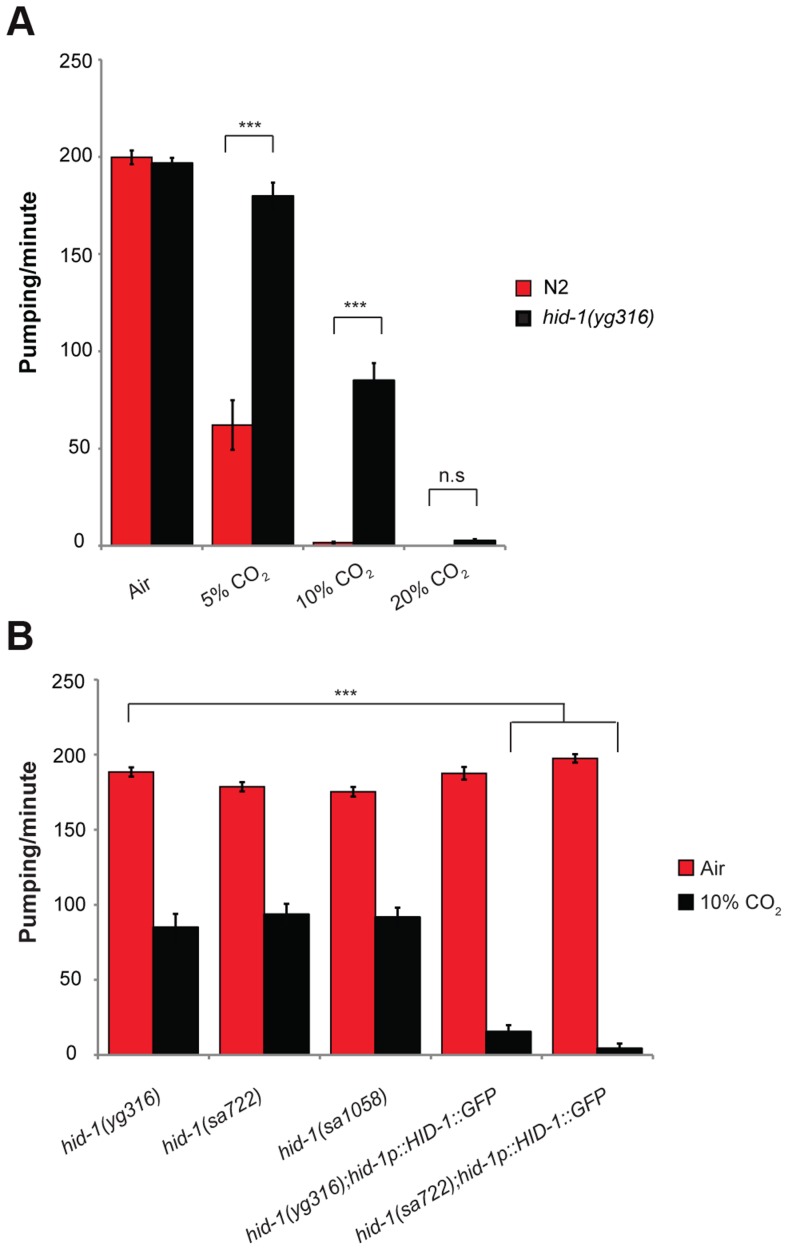
Figure 3. HID-1 is required for sensing CO2 level in the pharynx.
(A) One-day-old adult hid-1(yg316) and N2 worms were exposed to 5%, 10%, or 20% CO2 balanced with 21% O2 and N2. The pumping rate was measured under a dissecting microscope while the animals were exposed to the different gas mixtures. A gas mixture of 21% O2 and 79% N2 was used as a normal air control. (B) The inhibition of the pumping rate of the pharynx after exposure to high CO2 level in hid-1(yg316) allele mutants is significantly reduced. Similarly, the inhibition of the pumping rate of the pharynx after exposure to high CO2 level is reduced in other hid-1 allele mutants (sa772 and sa1058). Transgenic expression of HID-1 fused to eGFP in the sa722 or yg316 background (hid-1(sa722);HID-1::GFP or hid-1(yg316);HID-1::GFP) is sufficient to restore the effect of high CO2 level on the pumping rate back to the wild-type phenotype. In all experiments N≥30 animals. Different groups were compared by one-way ANOVA followed by t test. ***P<.001. Error bars indicate SEM.