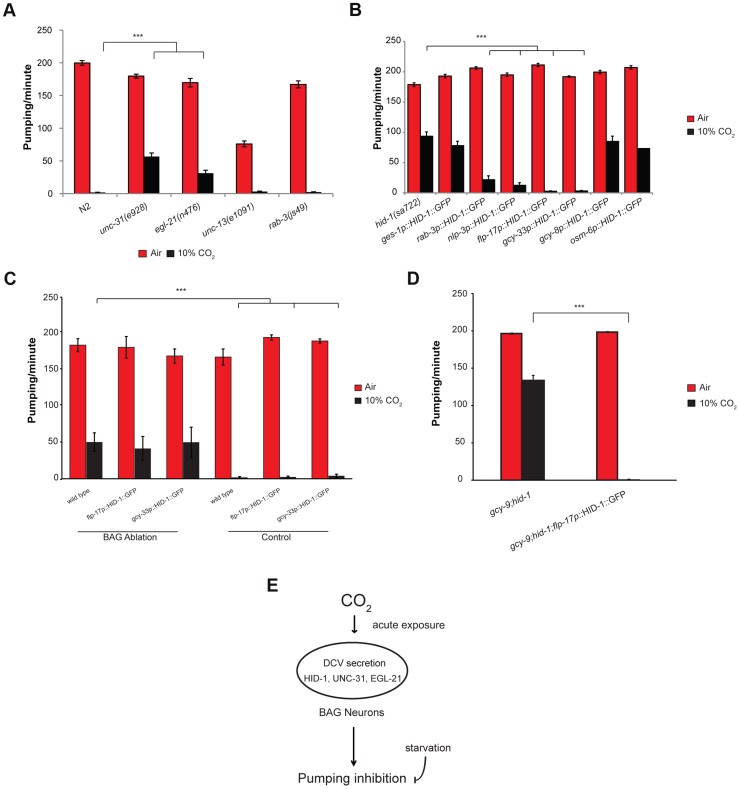
Figure 4. The effect of high CO2 level on the pharynx requires HID-1 activity in the BAG neurons.
(A) One-day-old adult C. elegans strains containing mutations in unc-31 or egl-21 genes, which are important for proper neuropeptide secretion and maturation, show a significant rescue of the pumping rate after exposure to 10% CO2. In contrast, strains with mutations in unc-13 or rab-3, which promote synaptic vesicle secretion, do not show a changed pharynx response to 10% CO2. (B) Transgenic expression of HID-1 in the gut using the gut-specific ges-1 promoter (ges-1p-HID-1::GFP) was not sufficient to restore pumping phenotype to wild type after exposure to 10% CO2. In contrast, transgenic expression of HID-1 in neurons using the rab-3 promoter (rab-3p-HID-1::GFP) was sufficient to restore pumping rate after exposure to 10% CO2 almost back to wild-type levels. Cell-specific expression of HID-1 in the AFD neurons (gcy-8p-HID-1::GFP) or in the amphid and tail ciliated neurons, including ASE neurons (osm-6p-HID-1::GFP), did not restore the CO2 effect on the pumping back to wild-type levels, whereas cell-specific expression of HID-1 in sensory and pharyngeal neurons (nlp-3p-HID-1::GFP) or in BAG neurons (flp-17p-HID-1::GFP and gcy-33p-HID-1::GFP) was sufficient to restore the effect of high CO2 level back to the wild-type phenotype. (C) The BAG neurons of wild-type C. elegans expressing gcy-33::GFP were laser ablated and the pharyngeal pumping rate was measured in normal air and 10% CO2. Similarly, the BAG neurons of flp-17p::HID-1::GFP and gcy-33p::HID-1::GFP strains were laser ablated and the pharyngeal pumping rate subsequently measured. Controls include measurement of the pumping rate in the same C. elegans strains without ablation. (D) Transgenic expression of HID-1 in the BAG neurons of hid-1(sa722);gcy-9(tm2816) animals restores the suppression of pumping in the presence of high CO2 level. (E) Schematic model of CO2 response of pharyngeal muscle contraction. The inhibition of muscle contraction in the pharynx is mediated by neuropeptide secretion via dense core vesicles (DCVs) in BAG neurons. The CO2 response is decreased after starvation. In all experiments N≥30 animals, except in panel C in flp-17p::HID-1::GFP (N = 5) and gcy-33p::HID-1::GFP (N = 10). Different groups were compared by one-way ANOVA followed by t test. ***P<.001. Error bars indicate SEM.