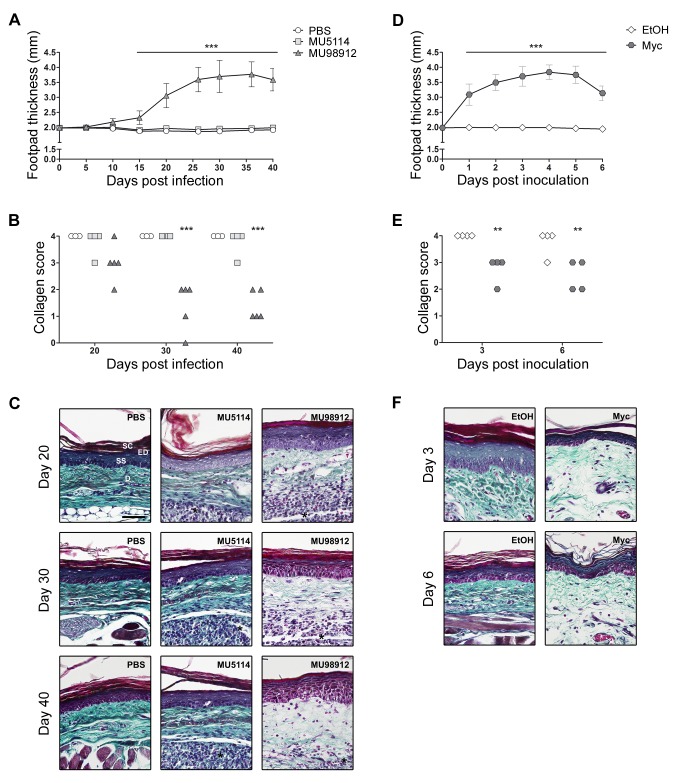
Figure 6. Mycolactone induces a decrease in dermal collagen fibers.
Mice were infected with virulent mycolactone-secreting (MU98912: dark gray triangles) (n = 5) or avirulent mycolactone-negative (MU5114: light gray squares) (n = 4) strains of M. ulcerans, or injected with PBS (vehicle: white circles) (n = 3) as a control (A, B and C). Alternatively, mice were inoculated with 5 µg of mycolactone (dark gray hexagons) (n = 4) or ethanol (vehicle: white diamonds) (n = 4) as a control (D, E, F). Lesion progression was assessed by measurement of footpad swelling (A and D). Collagen content was assessed by a qualitative blind scoring of the amount of dermal collagen fibers (score 0 = lowest, 4 = highest) visualized in HE-stained sections by polarized light (B and E). The different groups were compared to the control groups (PBS in A and B; ethanol in C and D) by Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest; statistical differences were represented by ** (P<0.01) or *** (P<0.001). Additionally, mouse footpads exposed to the different stimuli were stained with Masson's trichrome to highlight collagen fibers (green) (C and F). On panel are depicted representative histological image each group. Black horizontal bars represent a 50 µm scale. Histological structures like dermis (D) and the stratum corneum (SC) and stratum spinosum (SS) of the epidermis (ED) are indicated on the upper-left image. Inflammatory infiltrate is indicated by an asterisk.