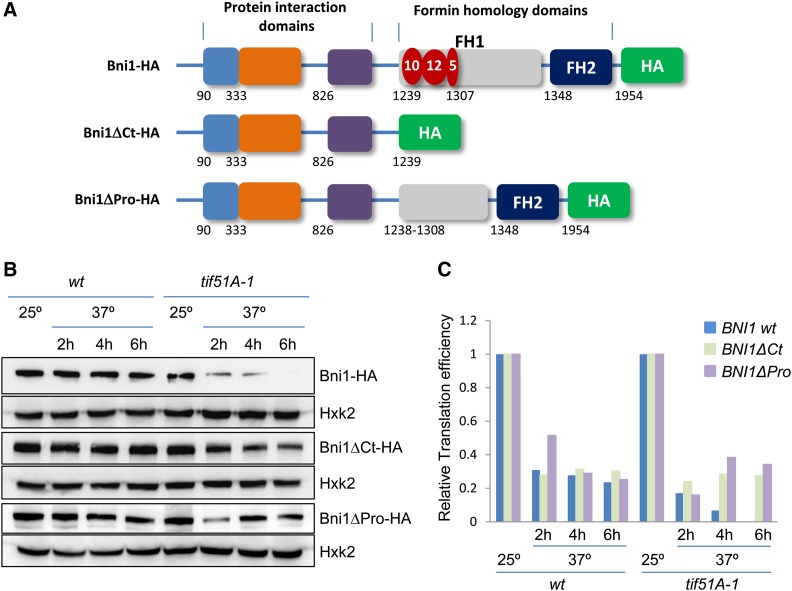
Figure 6.
Translation of the proline stretches of the formin BNI1 requires eIF5A. (A) Schematic diagrams showing C-terminal HA genomic tagging of full-length (BNI1-HA), C-terminal truncated (Δ1240–1954, BNI1ΔCt-HA), and proline-deleted (Δ1239–1307, BNI1ΔPro-HA) Bni1. Formin homology (FH) and protein interaction domains are indicated, as well as the polyPro stretches with the number of consecutive prolines represented in red. The numbers below the boxes indicate the first amino acid of each domain or stretch. (B) Immunoblots with antibodies against HA and hexokinase 2 protein (Hxk2) to show expression of full-length Bni1, C-terminal truncated Bni1, proline-deleted Bni1 and Hxk2, in wild type and tif51A-1 at 25° or 37° at the indicated times. (C) Translation efficiency of BNI1-HA, BNI1ΔCt-HA, and BNI1ΔPro-HA relative to translation efficiency of HXK2 in wild type and tif51A-1. Protein/mRNA ratios for Bni1, Bni1ΔCt-HA, Bni1ΔPro-HA, and Hxk2 were calculated by Western (B) and quantitative PCR from the same samples. Translation efficiencies of BNI1-HA, BNI1ΔCt-HA, and BNI1ΔPro-HA are calculated relative to translation efficiency of HXK2 and represented as a fraction against 25° for each strain.