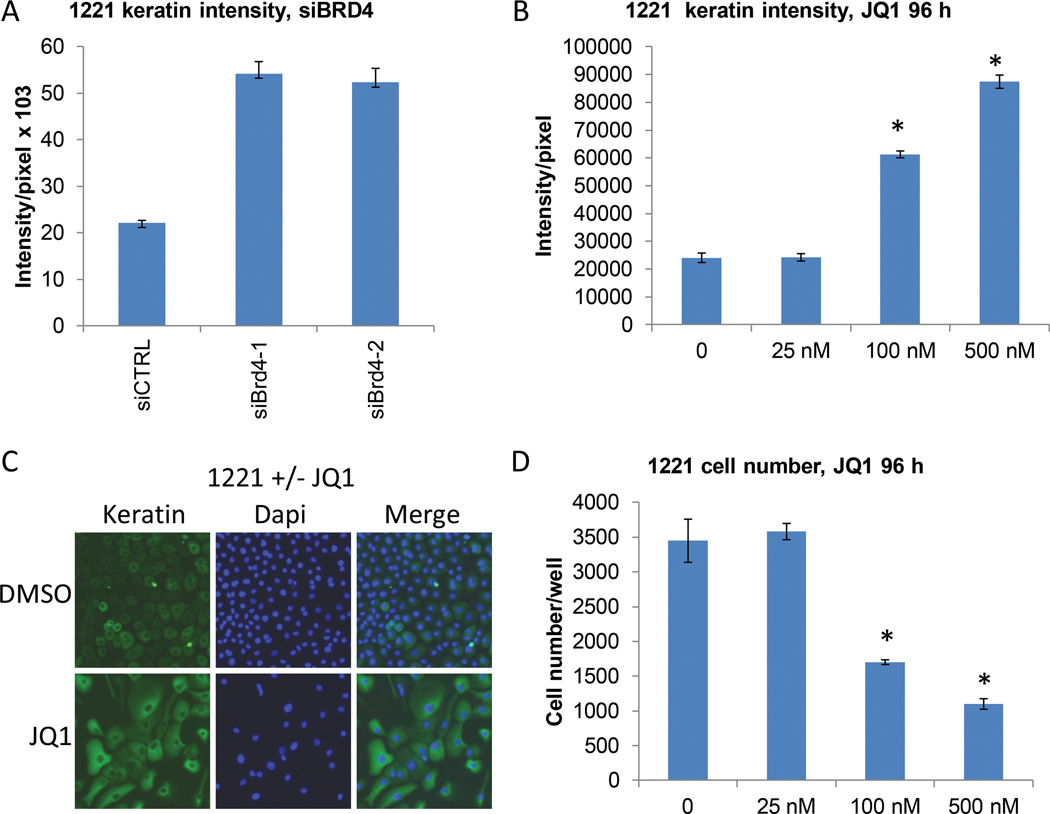
Figure 7. BRD4 inhibition arrests proliferation and induces differentiation of NSD3-NUT-expressing NMC cells.
(A) Using the 384-well plate high-throughput assay exhibited in Figure 2A, quantitative analysis of keratin intensity was compared in 1221 cells 72 h following transfection with control versus BRD4 siRNAs. Representative results from one of three biological replicates, each performed in triplicate, are shown. Error bars indicate the mean ± SD of triplicate wells.
(B) Using the high-throughput assay (above), quantitative analysis of keratin intensity was compared in 1221 cells 72 h following treatment with a dose range of JQ1 versus DMSO vehicle control. Results are the average of three biological replicates performed using the 384-well high throughput assay, each performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate the mean ± SD of the three biological replicates.* p <0.01
(C) Representative immunofluorescence microscopy of 1221 cells treated as in (B), with vehicle control or 500nM JQ1 for 72h. All photos are identical magnification (400×).
(D) Cell number using the high-throughput assay comparing 1221 cells 72 h following treatment with increasing concentrations of JQ1 versus DMSO vehicle control. Results are the average of three biological replicates, each performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate the mean ± SD of the three biological replicates.* p <0.01