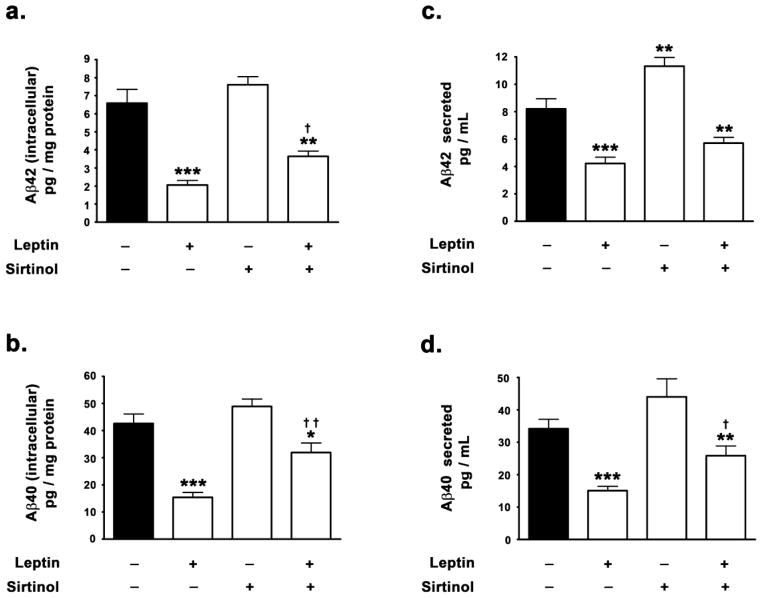
Figure 4. Leptin induced reduction in Aβ levels is partially contingent on SIRT1 activation.
(a,b) ELISA immunoassay clearly demonstrates that leptin significantly decreases the levels of intracellular Aβ42 and Aβ40, while concomitant treatment with the SIRT1 inhibitor sirtinol mitigates the leptin-induced decrease in intracellular Aβ42 and Aβ40. (c,d) ELISA immunoassay clearly shows that leptin significantly decreases the levels of secreted forms of Aβ42 and Aβ40, while co-treatment with the SIRT1 inhibitor sirtinol significantly attenuates the leptin-induced decrease in secreted Aβ42 and Aβ40. Data is expressed as Mean + S.E.M and includes determinations made in four separate cell culture experiments (n=4). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 versus control; † p<0.05, †† p<0.01 versus leptin.