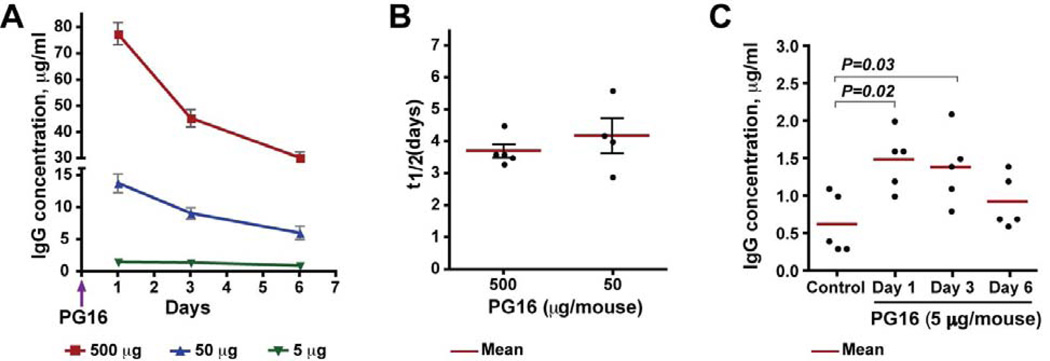
Fig. 1. PG16 serum half-life after a single administration of 5, 50, or 500 µg in SCID-hu Thy/Liv mice.
(A) Mice were treated with PG16 by i.p. injection, and the level of human IgG was measured by pan-human IgG ELISA in mouse serum collected 1, 3, and 6 days after treatment. (B) PG16 mean t1/2 was 3.7 days for the 500-µg dose and 4.2 days for the 50-µg dose. (C) Untreated SCID-hu Thy/Liv mice (control) had low levels (mean of 0.6 µg/ml) of human IgG in their serum, so the t1/2 for the 5-µg PG16 dose could not be accurately determined. On the day after treatment with 5 µg PG16, the mean human IgG concentration was 1.5 µg/ml, a portion of which (0.3–1.1 µg/ml) was nonspecific human IgG, as demonstrated by the low levels in serum from untreated control SCID-hu Thy/Liv mice.